Life insurance is a valuable financial tool that can provide peace of mind and financial security for your loved ones. However, it’s important to be aware of the potential tax implications of life insurance so that you can make informed decisions about your policy.
In this article, we’ll discuss the different types of life insurance policies and their tax implications, as well as how life insurance can be used for estate planning and business purposes. We’ll also provide some guidance on how to avoid common tax pitfalls related to life insurance.
Tax Implications of Life Insurance Policies
Life insurance is a financial tool that provides a death benefit to beneficiaries upon the insured’s death. It can also provide living benefits, such as cash value and loans. The tax implications of life insurance vary depending on the type of policy and how it is used.
There are two main types of life insurance policies: term life insurance and permanent life insurance. Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period of time, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. Permanent life insurance provides coverage for the insured’s entire life.
Taxation of Life Insurance Proceeds
The death benefit from a life insurance policy is generally not taxable to the beneficiaries. This is true regardless of the type of policy or how the proceeds are used. However, there are some exceptions to this rule. For example, if the death benefit is paid to the insured’s estate, it may be subject to estate taxes.
Tax Treatment of Life Insurance Cash Value and Loans
The cash value of a life insurance policy is the amount of money that has accumulated in the policy over time. The cash value can be borrowed against or withdrawn from the policy. Loans from a life insurance policy are not taxable, but withdrawals are. Withdrawals from a life insurance policy are taxed as ordinary income.
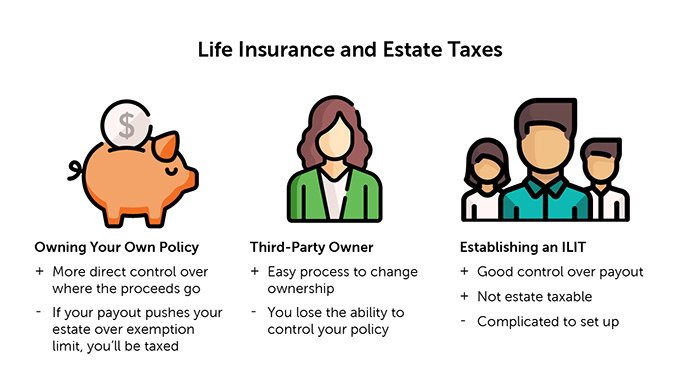
Life Insurance and Estate Planning
Life insurance can be a valuable tool for estate planning. It can be used to reduce estate taxes, fund trusts, and provide liquidity for beneficiaries.
Reducing Estate Taxes
Life insurance proceeds are generally not subject to estate taxes. This means that life insurance can be used to reduce the size of an estate and the amount of taxes that are owed.
Funding Trusts
Life insurance can be used to fund trusts. This can be a good way to provide for beneficiaries who are not yet able to manage their own finances. The trustee of the trust can use the life insurance proceeds to pay for the beneficiary’s education, medical expenses, or other needs.
Providing Liquidity
Life insurance can provide liquidity for beneficiaries. This can be helpful for paying estate taxes, funeral expenses, and other debts.
Structuring Life Insurance Policies for Estate Planning Purposes
There are a number of factors to consider when structuring life insurance policies for estate planning purposes. These factors include:
- The amount of coverage needed
- The type of policy
- The beneficiary
- The tax implications
It is important to work with an experienced estate planning attorney to ensure that life insurance policies are structured in a way that meets the specific needs of the individual.
Life Insurance for Business Owners
Life insurance can play a significant role in the financial planning of business owners. It provides a range of tax benefits and can be used to address specific business needs, such as key person protection, funding buy-sell agreements, and business succession planning.
Key Person Protection
Key person insurance protects a business against the financial impact of the death or disability of a key employee. The proceeds of the policy can be used to cover lost profits, replace the employee’s salary, or fund the recruitment and training of a replacement.
Buy-Sell Agreements
A buy-sell agreement is a legal agreement between business partners that Artikels the terms of the purchase and sale of each partner’s interest in the business in the event of death or disability. Life insurance can be used to fund the purchase of the deceased or disabled partner’s interest, ensuring a smooth transition of ownership.
Business Succession Planning
Life insurance can be used to fund business succession planning by providing funds for the purchase of the business by a family member, employee, or third party. This ensures that the business can continue to operate smoothly and preserve the legacy of the business owner.
Special Considerations
When considering the tax implications of life insurance, it is essential to be aware of special considerations that may apply in certain situations.
Tax Implications for Non-Residents
For non-residents, the tax treatment of life insurance proceeds can vary depending on the country of residence and the specific tax laws applicable. It is advisable to consult with a tax professional to understand the tax implications in your specific situation.
Tax Treatment of Life Insurance Proceeds in the Event of a Divorce
In the event of a divorce, the tax treatment of life insurance proceeds can be complex. Generally, if the policy was owned by one spouse before the marriage, the proceeds may be considered separate property and not subject to division. However, if the policy was acquired during the marriage, the proceeds may be considered marital property and subject to division.
Avoiding Common Tax Pitfalls Related to Life Insurance
To avoid common tax pitfalls related to life insurance, it is important to:
- Understand the tax implications of different types of life insurance policies.
- Consider the tax consequences of naming beneficiaries.
- Be aware of the potential tax liability if you borrow against the cash value of a policy.
Final Summary
Life insurance is a complex financial product with a variety of potential tax implications. It’s important to work with a qualified financial advisor to understand the tax implications of your policy and to make sure that it meets your financial goals.
Q&A
What are the different types of life insurance policies?
There are two main types of life insurance policies: term life insurance and whole life insurance. Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period of time, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. Whole life insurance provides coverage for your entire life, as long as you continue to pay the premiums.
How are life insurance proceeds taxed for beneficiaries?
Life insurance proceeds are generally not taxable for beneficiaries. However, there are some exceptions to this rule. For example, if the proceeds are used to pay off a loan that was secured by the life insurance policy, the proceeds may be taxable.
How is the cash value of a life insurance policy taxed?
The cash value of a life insurance policy is taxed as ordinary income when it is withdrawn. However, there are some exceptions to this rule. For example, if the cash value is used to pay for qualified education expenses, it may be tax-free.
How are loans from a life insurance policy taxed?
Loans from a life insurance policy are not taxable. However, if the loan is not repaid, the proceeds of the policy may be reduced by the amount of the outstanding loan.