In the realm of HVAC engineering, precision is paramount. HVAC load calculations and sizing software have emerged as indispensable tools, empowering engineers to optimize system design, minimize energy consumption, and ensure occupant comfort. This article delves into the capabilities, benefits, and considerations associated with these powerful software solutions.
From defining the software’s purpose to exploring its advanced applications, we will unravel the intricate world of HVAC load calculation and sizing software. Discover how this technology revolutionizes the design process, enabling engineers to tackle complex projects with confidence and efficiency.
Software Overview
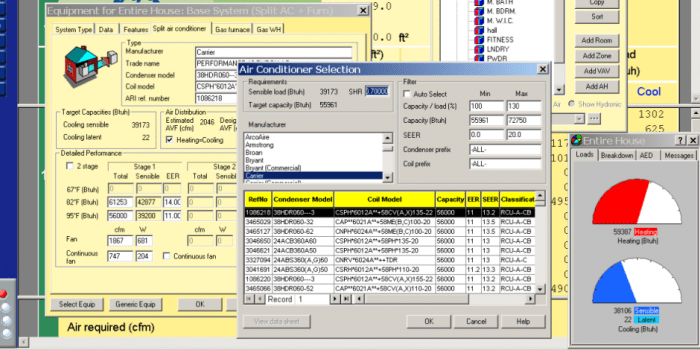
HVAC load calculations and sizing software are specialized tools designed to assist engineers and contractors in determining the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) requirements of buildings. These software programs utilize advanced algorithms and databases to calculate the heat transfer rates, airflow rates, and equipment capacities necessary to maintain comfortable indoor environments.The
use of HVAC load calculations and sizing software offers numerous benefits. By automating complex calculations, these programs save time and reduce the risk of errors. They also provide accurate and reliable results, ensuring that HVAC systems are designed to meet the specific needs of each building.
Additionally, these software tools often include features such as equipment selection, cost estimation, and reporting, which further streamline the design process.
Commonly Used Software
The HVAC industry utilizes a wide range of software programs for load calculations and sizing. Some of the most commonly used options include:
- Carrier HAP
- Trane Trace
- Revit MEP
- IESVE
- DOE-2
Features and Capabilities
HVAC load calculation and sizing software offers a comprehensive suite of features and capabilities designed to streamline the design and optimization of HVAC systems. These software solutions empower engineers and contractors to perform complex calculations, analyze system performance, and make informed decisions throughout the HVAC system lifecycle.
Key features and capabilities include:
- Load calculations: Software can calculate heating and cooling loads for various building types and climates, considering factors such as building envelope, occupancy, and equipment.
- System sizing: Based on load calculations, software can size HVAC equipment, including chillers, boilers, air handlers, and ductwork, to meet the specific requirements of the building.
- Energy analysis: Software can simulate system performance and predict energy consumption, enabling engineers to evaluate different design options and optimize system efficiency.
- Optimization tools: Advanced software features, such as parametric analysis and optimization algorithms, can help engineers explore design alternatives and identify the most efficient and cost-effective solutions.
- Reporting and documentation: Software can generate detailed reports and documentation, including load calculations, system sizing, and energy analysis results, for easy sharing and compliance with building codes.
Types of Calculations and Analyses
HVAC load calculation and sizing software can perform a wide range of calculations and analyses, including:
- Heat loss and heat gain calculations: Software can calculate the heat loss or heat gain through building envelope components, such as walls, roofs, windows, and doors, based on factors such as construction materials, insulation levels, and climate data.
- Airflow calculations: Software can calculate airflow rates, pressure drops, and fan power requirements for duct systems, ensuring proper air distribution and ventilation.
- Psychrometric analysis: Software can perform psychrometric calculations to determine the properties of air, such as temperature, humidity, and enthalpy, which is essential for designing and sizing air conditioning and dehumidification systems.
- Energy consumption analysis: Software can simulate system performance over time, taking into account factors such as occupancy schedules, weather conditions, and equipment efficiency, to predict energy consumption and identify opportunities for energy savings.
Optimizing System Design and Efficiency
HVAC load calculation and sizing software plays a crucial role in optimizing HVAC system design and efficiency. By providing accurate and detailed calculations, the software helps engineers make informed decisions about equipment selection, system configuration, and control strategies.
Key benefits include:
- Improved system performance: Accurate load calculations and system sizing ensure that HVAC systems meet the specific requirements of the building, resulting in optimal comfort levels and energy efficiency.
- Reduced energy consumption: Energy analysis capabilities help engineers identify and implement energy-saving measures, such as variable-speed drives, high-efficiency equipment, and demand-controlled ventilation.
- Enhanced occupant comfort: Proper load calculations and system design ensure that HVAC systems provide a comfortable and healthy indoor environment, meeting the needs of occupants.
- Reduced operating costs: Optimized system design and energy efficiency can significantly reduce operating costs over the life of the HVAC system.
- Compliance with building codes: Software can generate reports and documentation that meet building code requirements, ensuring compliance and facilitating the approval process.
Benefits and Advantages
HVAC load calculation and sizing software offers numerous benefits and advantages that can significantly enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness of HVAC system design and operation.
By leveraging advanced algorithms and industry-standard methodologies, this software automates complex calculations, reducing the time and effort required for manual calculations. This automation also minimizes errors, ensuring more precise and reliable results.
Quantifiable Savings
The use of HVAC load calculation and sizing software can lead to substantial savings in time, cost, and energy consumption. By accurately determining the heating and cooling loads of a building, the software helps optimize system design, resulting in reduced equipment sizing and operating costs.
For instance, a study by the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) found that using load calculation software can reduce energy consumption by up to 15% in commercial buildings.
Case Studies
Numerous case studies have demonstrated the successful implementation of HVAC load calculation and sizing software in various applications.
- In a hospital project, the software helped reduce the size of the HVAC system by 20%, resulting in significant cost savings on equipment and installation.
- For a large office building, the software optimized the design of the HVAC system, leading to a 10% reduction in energy consumption and a corresponding decrease in operating costs.
Selection Criteria
Selecting the right HVAC load calculation and sizing software is crucial for accurate and efficient HVAC system design. Consider the following key factors:
-
-*System Type
Choose software that supports the types of HVAC systems you design, including residential, commercial, or industrial.
-*Load Calculation Methods
Ensure the software employs industry-standard load calculation methods, such as ASHRAE, ACCA, or CIBSE.
-*Sizing Capabilities
Verify that the software can size equipment, including air handlers, chillers, and boilers, based on calculated loads.
-*User Interface
Opt for software with an intuitive and user-friendly interface, minimizing learning curves and improving efficiency.
-*Reporting Capabilities
Choose software that generates comprehensive reports detailing load calculations, equipment sizing, and energy consumption estimates.
-*Compatibility
Ensure compatibility with existing software systems, such as CAD or BIM, to streamline workflows.
-*Technical Support
Consider the availability and quality of technical support provided by the software vendor.
Software Comparison Checklist
To compare different software options, use a checklist that includes the following criteria:
- System types supported
- Load calculation methods used
- Sizing capabilities
- User interface
- Reporting capabilities
- Compatibility
- Technical support
Implementation and Use
Implementing and utilizing HVAC load calculation and sizing software involves several key steps. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the process, from data collection to reporting.
To ensure accurate and efficient use of the software, it is crucial to follow a structured workflow and adhere to best practices.
Data Collection
Data collection is the foundation for accurate load calculations and sizing. Gather comprehensive information on the building’s characteristics, including:
- Building envelope (walls, roof, windows)
- Occupancy and usage patterns
- Internal heat gains (appliances, lighting)
- Climate data (temperature, humidity)
Analysis and Modeling
Input the collected data into the software. The software will perform calculations based on industry standards and algorithms, considering factors such as:
- Heat transfer through the building envelope
- Internal heat gains
- Outdoor climate conditions
The software will generate a detailed report outlining the calculated heating and cooling loads for each zone or space within the building.
Equipment Sizing
Based on the load calculations, the software can assist in sizing the appropriate HVAC equipment, including:
- Air conditioners
- Heat pumps
- Boilers
- Ductwork
The software will provide recommendations based on industry standards and the specific requirements of the building.
Reporting and Documentation
The software will generate comprehensive reports that include:
- Load calculations
- Equipment sizing recommendations
- Energy efficiency analysis
These reports provide valuable documentation for design, installation, and maintenance purposes.
Advanced Applications
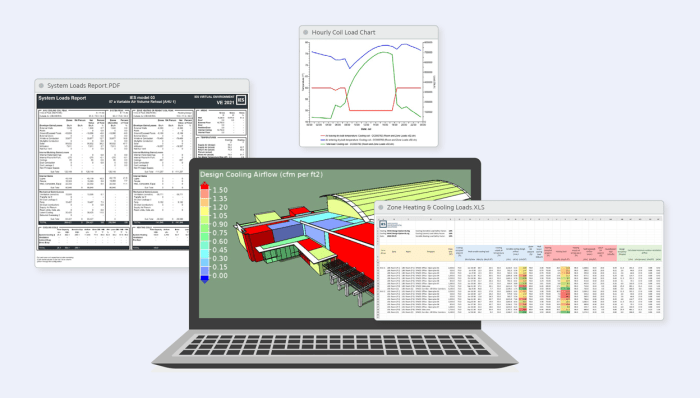
HVAC load calculation and sizing software has advanced beyond its traditional applications. It now offers a range of advanced capabilities that enable engineers to perform complex tasks and optimize system performance.
One of the most significant advancements is the ability to use the software for system simulation. This allows engineers to create a virtual model of their HVAC system and test different operating scenarios without making any physical changes. This can be invaluable for troubleshooting existing systems or designing new ones, as it allows engineers to identify potential problems and optimize performance before any equipment is installed.
Energy Modeling
Another advanced application of HVAC load calculation and sizing software is energy modeling. This software can be used to estimate the energy consumption of a building or system, taking into account factors such as climate, building envelope, and HVAC equipment efficiency.
This information can be used to make informed decisions about energy-saving measures, such as insulation upgrades or equipment retrofits.
Fault Detection
HVAC load calculation and sizing software can also be used for fault detection. This software can monitor system performance data and identify potential problems, such as refrigerant leaks or equipment malfunctions. This information can be used to schedule maintenance or repairs before they become major issues, helping to prevent downtime and costly repairs.
Innovative Uses
In addition to these advanced applications, HVAC load calculation and sizing software is also being used in a number of innovative ways in the industry. For example, some software programs can now be used to generate 3D models of HVAC systems, which can be helpful for visualizing the system and identifying potential problems.
Other software programs can be used to integrate HVAC systems with other building systems, such as lighting and security systems. This can help to improve overall building performance and efficiency.
Final Thoughts
HVAC load calculation and sizing software has transformed the HVAC industry, providing engineers with a comprehensive suite of tools to design and optimize systems. By embracing this technology, engineers can unlock significant savings in time, cost, and energy, while ensuring the comfort and well-being of building occupants.
As the industry continues to evolve, these software solutions will undoubtedly play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of HVAC design.
Answers to Common Questions
What is HVAC load calculation and sizing software?
HVAC load calculation and sizing software is a specialized tool designed to assist engineers in determining the heating and cooling loads of a building. It helps determine the appropriate size and capacity of HVAC equipment, ensuring optimal system performance and energy efficiency.
What are the benefits of using HVAC load calculation and sizing software?
HVAC load calculation and sizing software offers numerous benefits, including reduced design time, improved accuracy, optimized system performance, and significant energy savings. It streamlines the design process, minimizes errors, and helps engineers create more efficient and cost-effective HVAC systems.
What are some common features of HVAC load calculation and sizing software?
Common features of HVAC load calculation and sizing software include the ability to perform heating and cooling load calculations, equipment sizing, ductwork design, and energy analysis. Some software also offers advanced features such as system simulation, fault detection, and integration with building information modeling (BIM) software.
How do I select the right HVAC load calculation and sizing software for my needs?
When selecting HVAC load calculation and sizing software, consider factors such as the size and complexity of your projects, the features and capabilities required, compatibility with your existing systems, and the level of technical support provided. It’s advisable to evaluate different software options and choose the one that best meets your specific requirements.