In the realm of building management, HVAC systems play a pivotal role in maintaining optimal indoor environments. However, optimizing their performance and ensuring occupant comfort can be a daunting task. HVAC software with reporting and analytics capabilities emerges as a game-changer, providing facility managers with the tools to unlock unprecedented insights and drive operational excellence.
With advanced reporting features and robust analytics, HVAC software empowers users to monitor system performance, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions. Join us as we delve into the transformative benefits of HVAC software with reporting and analytics, exploring how it can revolutionize building operations and enhance occupant well-being.
HVAC Software Overview
HVAC software is a specialized tool designed to assist professionals in the design, analysis, and optimization of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. It provides comprehensive capabilities for modeling, simulation, and analysis, enabling engineers and technicians to make informed decisions and improve the efficiency and performance of HVAC systems.
Key features and benefits of using HVAC software include:
- Accurate modeling and simulation of HVAC systems, allowing for precise analysis of system performance under various operating conditions.
- Optimization of system design, resulting in reduced energy consumption, improved comfort levels, and enhanced indoor air quality.
li>Automated generation of reports and documentation, saving time and ensuring accuracy.
Different types of HVAC software are available, each tailored to specific needs and applications. These include:
- System design software: Used for creating detailed models of HVAC systems, including equipment selection, ductwork design, and control strategies.
- Simulation software: Used for predicting the performance of HVAC systems under different operating conditions, such as varying loads, weather conditions, and occupancy patterns.
- Analysis software: Used for evaluating the efficiency and effectiveness of HVAC systems, identifying areas for improvement, and optimizing system performance.
Reporting and Analytics Capabilities
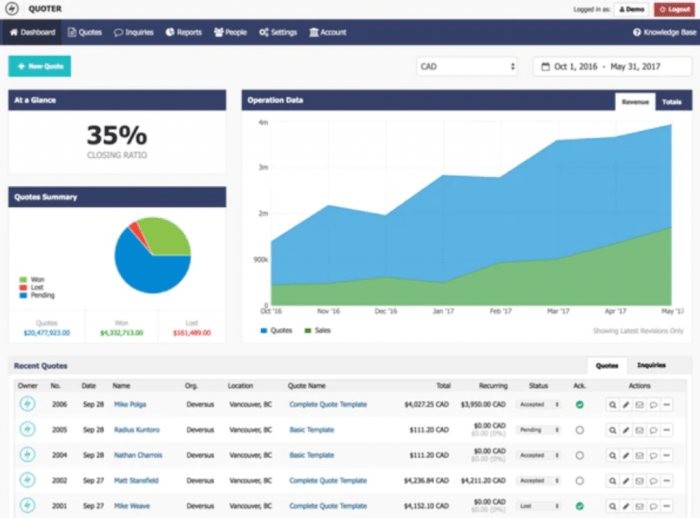
HVAC software provides robust reporting capabilities that enable users to track and analyze system performance. These reports can help identify areas for improvement, reduce energy consumption, and optimize maintenance schedules.
The types of reports that can be generated include:
- Energy consumption reports track the amount of energy used by the HVAC system over time. This data can be used to identify trends and inefficiencies, and to make informed decisions about how to reduce energy consumption.
- Equipment performance reports track the performance of individual HVAC components, such as chillers, boilers, and air handlers. This data can be used to identify problems early on, and to schedule maintenance accordingly.
- Maintenance reports track the maintenance history of the HVAC system. This data can be used to ensure that all maintenance tasks are being performed on schedule, and to identify any recurring problems.
Analytics for HVAC System Performance Improvement
In addition to reporting, HVAC software also provides analytics capabilities that can be used to improve system performance. These analytics tools can help users:
- Identify trends and patterns in system data.
- Develop predictive models to forecast future system performance.
- Optimize system settings to improve efficiency and comfort.
By using the reporting and analytics capabilities of HVAC software, users can gain a deep understanding of their system’s performance. This information can be used to make informed decisions about how to improve system performance, reduce energy consumption, and extend the life of the equipment.
Benefits of Using HVAC Software with Reporting and Analytics
HVAC software with reporting and analytics capabilities offers a range of benefits that can significantly enhance the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and occupant comfort of HVAC systems. By leveraging data analysis and visualization, these software solutions provide valuable insights that enable informed decision-making and optimization.
One of the key benefits of using HVAC software is its ability to reduce operating costs. Through continuous monitoring and analysis of system performance, the software identifies areas for improvement, such as inefficiencies in equipment operation or energy consumption patterns.
This data-driven approach allows facility managers to make targeted adjustments and optimizations, resulting in significant cost savings.
Energy Efficiency
HVAC software plays a crucial role in improving energy efficiency. By analyzing energy consumption data, the software identifies patterns and trends that reveal inefficiencies in system operation. It can also simulate different operating scenarios to evaluate the potential impact of changes, such as adjusting temperature set points or implementing demand-controlled ventilation.
This enables facility managers to make informed decisions that maximize energy efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
Occupant Comfort
HVAC software contributes to enhanced occupant comfort by providing real-time insights into indoor environmental conditions. By monitoring temperature, humidity, and air quality, the software can identify areas where comfort levels are compromised. This data enables facility managers to make adjustments to the HVAC system to optimize conditions for occupant well-being and productivity.
Implementation and Integration
Implementing HVAC software effectively requires a systematic approach and careful planning. It involves selecting the right software, configuring it according to specific requirements, training staff, and integrating it with other relevant systems.
Integrating HVAC software with other systems, such as building management systems (BMS) and energy management systems (EMS), is crucial for optimizing energy efficiency and reducing operational costs. By sharing data and automating processes, integration enables a comprehensive view of building performance and allows for proactive maintenance and optimization.
Best Practices
- Conduct a thorough needs assessment to identify specific requirements and goals.
- Select software that aligns with organizational objectives and technical capabilities.
- Involve key stakeholders and users in the implementation process to ensure buy-in and adoption.
- Provide comprehensive training to staff on software functionality and best practices.
- Integrate the software with other relevant systems to maximize its value and efficiency.
- Establish clear roles and responsibilities for software management and maintenance.
- Monitor and evaluate software performance regularly to identify areas for improvement.
Case Studies and Success Stories
HVAC software implementations have led to remarkable success stories across various industries. These case studies demonstrate the tangible benefits of leveraging technology to optimize HVAC systems.
By analyzing real-world examples, we can gain valuable insights into how HVAC software has transformed operations and reduced costs.
Improved Energy Efficiency
- A manufacturing facility implemented HVAC software and achieved a 20% reduction in energy consumption, resulting in significant cost savings.
- A commercial building reduced its energy bills by 15% after installing HVAC software that optimized temperature control and equipment scheduling.
Enhanced Comfort and Productivity
- A school district deployed HVAC software and improved indoor air quality, leading to a 10% increase in student attendance and reduced absenteeism due to illness.
- An office building installed HVAC software and reported a 12% increase in employee productivity due to improved temperature and humidity control.
Reduced Maintenance Costs
- A healthcare facility implemented HVAC software and extended the lifespan of its HVAC equipment by 15%, reducing maintenance and repair costs.
- A hotel chain installed HVAC software and reduced its maintenance workload by 25% through proactive monitoring and predictive maintenance alerts.
Customer Testimonials
Here’s what satisfied customers have to say about the benefits of using HVAC software with reporting and analytics:
“Our HVAC software has been a game-changer for our operations. We’ve saved a substantial amount of money on energy and maintenance costs, and our indoor air quality has improved significantly.”
Facility Manager, Manufacturing Company
“The HVAC software has given us complete visibility into our system. We can now identify and address potential issues before they become major problems.”
Maintenance Supervisor, Commercial Building
Future Trends and Advancements
The future of HVAC software is bright, with many emerging trends that will shape its development and impact on the industry. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are two of the most important trends, as they have the potential to revolutionize the way that HVAC systems are designed, operated, and maintained.
AI and ML can be used to improve the efficiency of HVAC systems, reduce energy consumption, and predict and prevent problems. For example, AI can be used to optimize the operation of chillers and boilers, while ML can be used to predict when equipment is likely to fail.
AI and ML in HVAC Software
AI and ML are already being used in a number of HVAC software applications. For example, some software programs use AI to optimize the operation of HVAC systems, while others use ML to predict when equipment is likely to fail.
As AI and ML continue to develop, we can expect to see even more innovative and groundbreaking applications of these technologies in the HVAC industry.
Impact on the Industry
The future of HVAC software is likely to have a significant impact on the industry. As software becomes more sophisticated and easier to use, it will become increasingly essential for HVAC professionals to have a strong understanding of software tools.
Software will also play a key role in the development of new and innovative HVAC technologies, such as smart buildings and self-driving HVAC systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, HVAC software with reporting and analytics is an indispensable tool for modern facility management. By providing real-time insights, enabling proactive maintenance, and optimizing energy consumption, it empowers organizations to achieve unparalleled levels of efficiency, comfort, and cost savings.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated and innovative solutions that will further revolutionize the HVAC industry. Embracing the power of HVAC software with reporting and analytics is a strategic investment in the future of building management, ensuring optimal performance, occupant satisfaction, and a sustainable built environment.
Helpful Answers
What are the key benefits of using HVAC software with reporting and analytics?
HVAC software with reporting and analytics offers numerous benefits, including cost savings through optimized energy consumption, improved energy efficiency, enhanced occupant comfort, predictive maintenance capabilities, and data-driven decision-making.
How does HVAC software with reporting and analytics improve energy efficiency?
By monitoring energy consumption patterns, identifying inefficiencies, and providing actionable insights, HVAC software helps facility managers make informed decisions to reduce energy waste and optimize system performance.
How can HVAC software with reporting and analytics enhance occupant comfort?
HVAC software with reporting and analytics enables facility managers to monitor and adjust temperature, humidity, and air quality levels, ensuring a comfortable and healthy indoor environment for occupants.
What are some common types of reports generated by HVAC software?
HVAC software generates a wide range of reports, including energy consumption reports, maintenance reports, performance reports, and fault detection reports, providing valuable insights into system operation and performance.