In the ever-evolving landscape of building design, the advent of HVAC software with load calculation capabilities has ushered in a new era of precision and efficiency. This transformative technology empowers engineers and contractors with the tools they need to optimize HVAC systems, ensuring maximum comfort, energy savings, and cost-effectiveness.
HVAC software with load calculation seamlessly integrates essential features, including load calculation methods, equipment selection and sizing, energy efficiency analysis, and project management tools, into a comprehensive and user-friendly platform. This enables professionals to streamline their workflows, enhance collaboration, and deliver exceptional results.
Software Overview
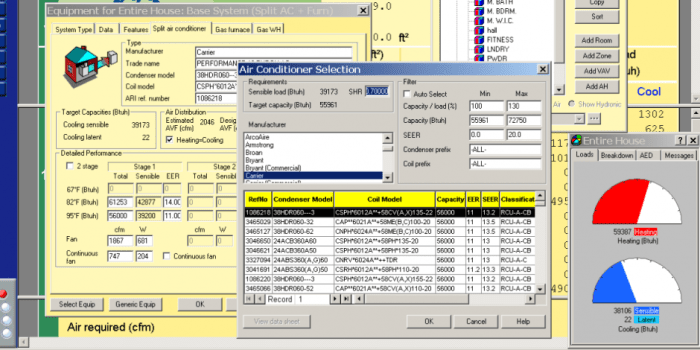
HVAC software with load calculation capabilities is a comprehensive tool designed to assist engineers and contractors in designing, analyzing, and optimizing HVAC systems. It provides a range of features to help users perform accurate load calculations, select appropriate equipment, and create detailed system designs.
The software typically includes a database of equipment performance data, weather data, and building construction information. This data is used to calculate heating and cooling loads for a given building, taking into account factors such as building orientation, insulation levels, and occupancy patterns.
Benefits of Using HVAC Software with Load Calculation
- Improved accuracy of load calculations, leading to more efficient and cost-effective system design.
- Reduced design time and effort, as the software automates many of the calculations and analysis tasks.
- Enhanced system performance, as the software can help identify and optimize system components to meet specific requirements.
- Improved documentation and reporting, as the software can generate detailed reports and drawings that can be used for project documentation and submission.
Key Features
HVAC software with load calculation provides essential features to streamline the design and analysis of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. These features empower engineers, contractors, and designers with tools to optimize system performance, ensure energy efficiency, and meet industry standards.
-
Load Calculation Methods
HVAC software utilizes various load calculation methods to accurately determine the heating and cooling requirements of a building. These methods include Manual J (Residential), ACCA (Air Conditioning Contractors of America), and ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers) standards, ensuring compliance with industry guidelines.
-
Equipment Selection and Sizing
The software assists in selecting and sizing appropriate HVAC equipment based on the calculated load requirements. It provides a comprehensive database of equipment options, allowing users to compare specifications, efficiency ratings, and dimensions to make informed decisions.
-
Energy Efficiency Analysis
Energy efficiency is a crucial aspect of HVAC system design. The software incorporates energy analysis tools that evaluate the efficiency of proposed systems, identify potential energy savings, and suggest measures to improve overall system performance.
-
Project Management Tools
HVAC software often includes project management tools to facilitate efficient workflow. These tools allow users to create and manage projects, track progress, collaborate with team members, and generate reports, streamlining the project lifecycle.
Load Calculation
The software provides comprehensive load calculation capabilities to accurately determine the heating, cooling, and ventilation requirements of buildings.
By considering factors such as building dimensions, climate data, and occupancy patterns, the software generates detailed load reports that are essential for designing and sizing HVAC systems.
Input Parameters
The software requires various input parameters to perform load calculations, including:
- Building geometry (dimensions, orientation, number of floors)
- Building materials (thermal properties, insulation levels)
- Climate data (temperature, humidity, solar radiation)
- Occupancy patterns (number of occupants, schedules)
- Equipment and lighting loads
Types of Load Calculations
The software can perform various types of load calculations, including:
- Heating load calculations to determine the amount of heat required to maintain indoor temperatures during cold weather.
- Cooling load calculations to determine the amount of cooling required to maintain indoor temperatures during warm weather.
- Ventilation load calculations to determine the amount of fresh air required for occupant health and comfort.
Output Reports
The software generates comprehensive load reports that provide detailed information about the calculated loads.
These reports include:
- Hourly load profiles for heating, cooling, and ventilation
- Peak load values and occurrence times
- Sensible and latent heat loads
- Internal and external heat gains
Interpretation of Results
The load calculation results are essential for designing and sizing HVAC systems that meet the specific requirements of the building.
By understanding the load profiles and peak load values, engineers can determine the appropriate capacity and type of HVAC equipment needed to provide optimal indoor comfort and energy efficiency.
Equipment Selection and Sizing
The software streamlines the process of selecting and sizing HVAC equipment based on the calculated loads. It provides comprehensive data on various equipment types, capacities, and efficiencies to ensure optimal system performance.
By leveraging its extensive manufacturers’ databases, the software allows users to access detailed specifications and performance data for a wide range of HVAC equipment. This integration facilitates informed decision-making and ensures compatibility with specific project requirements.
Equipment Types
The software supports a comprehensive range of HVAC equipment, including:
- Air conditioners (central, packaged, split systems)
- Furnaces (gas, electric, oil)
- Boilers (gas, electric, steam)
- Heat pumps (air-source, ground-source)
Capacity and Efficiency Considerations
The software assists in determining the appropriate capacity and efficiency of HVAC equipment based on the load calculations. It considers factors such as:
- Building size and layout
- Occupancy and usage patterns
- Climate zone and weather conditions
- Energy efficiency standards and regulations
By optimizing equipment capacity and efficiency, the software helps minimize energy consumption and operating costs while ensuring occupant comfort.
Energy Efficiency Analysis
The software provides comprehensive energy efficiency analysis capabilities, enabling users to optimize the performance of their HVAC systems and reduce energy consumption.
By leveraging advanced algorithms and data analysis techniques, the software offers a range of features to help users evaluate the energy efficiency of their systems, including:
Energy Consumption Tracking
- Monitors energy consumption over time, providing detailed insights into system performance and energy usage patterns.
- Identifies periods of peak energy demand and areas where energy consumption can be reduced.
Efficiency Metrics
- Calculates key efficiency metrics such as SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio), EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio), and AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency).
- Compares system efficiency to industry benchmarks and provides recommendations for improvement.
Recommendations for Energy-Saving Measures
- Generates personalized recommendations for energy-saving measures, such as equipment upgrades, system modifications, and operational adjustments.
- Estimates the potential energy savings and cost reductions associated with implementing these measures.
Project Management
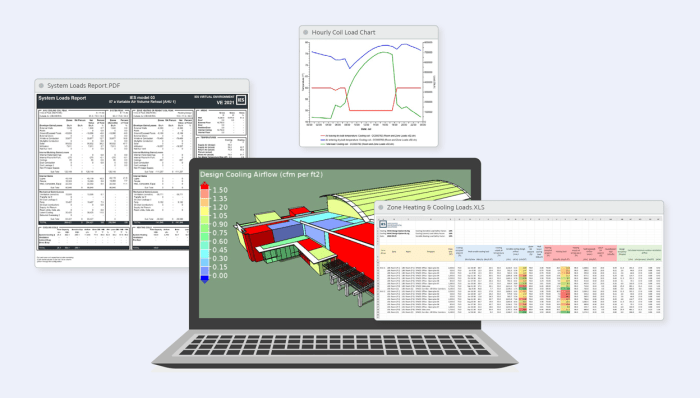
The software offers comprehensive project management capabilities to streamline your HVAC design workflow. It enables efficient project creation, tracking, and collaboration among team members.
Key project management features include:
Project Creation and Tracking
- Create and manage multiple HVAC projects simultaneously.
- Define project parameters, including project name, description, and timelines.
- Track project progress and identify potential bottlenecks or delays.
Collaboration Tools
- Share project documents, drawings, and specifications with team members.
- Facilitate communication and collaboration through integrated messaging and commenting features.
- Maintain a central repository for all project-related information, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
Reporting and Documentation Features
- Generate comprehensive project reports, including load calculations, equipment specifications, and energy analysis results.
- Export project data and reports in various formats for easy sharing and archiving.
- Maintain a detailed record of project decisions and changes for future reference and audit purposes.
Benefits of Using HVAC Software with Load Calculation
HVAC software with load calculation capabilities offers significant advantages for engineers and contractors involved in HVAC system design and installation. These benefits include:
Improved accuracy and efficiency in HVAC design: HVAC software utilizes advanced algorithms and industry-standard methods to calculate heating and cooling loads accurately. This precision ensures that the designed system meets the specific requirements of the building, reducing the risk of oversizing or undersizing the equipment.
By optimizing the system design, HVAC software helps minimize energy consumption and operating costs while enhancing occupant comfort.
Reduced energy consumption and operating costs
HVAC software with load calculation capabilities plays a crucial role in reducing energy consumption and operating costs for buildings. By accurately determining the heating and cooling loads, the software helps engineers select the most energy-efficient equipment and system configurations. This optimization ensures that the HVAC system operates at peak efficiency, reducing energy usage and lowering utility bills.
Additionally, load calculation software can identify areas where energy savings can be implemented, such as through the use of variable air volume (VAV) systems or heat recovery systems.
Enhanced project collaboration and documentation
HVAC software with load calculation capabilities facilitates seamless project collaboration and documentation. The software allows multiple users to work on the same project simultaneously, ensuring efficient communication and coordination among team members. The software also generates comprehensive reports and documentation that includes load calculations, equipment specifications, and system design details.
This documentation serves as a valuable resource for contractors, engineers, and building owners throughout the project lifecycle.
Conclusion
The benefits of leveraging HVAC software with load calculation are undeniable. By harnessing the power of these tools, engineers and contractors can achieve unprecedented levels of accuracy and efficiency in HVAC design, resulting in reduced energy consumption, lower operating costs, and enhanced project collaboration.
As the industry continues to evolve, HVAC software with load calculation will undoubtedly remain an indispensable asset, empowering professionals to deliver sustainable and cost-effective HVAC solutions.
Helpful Answers
What are the advantages of using HVAC software with load calculation?
HVAC software with load calculation offers numerous advantages, including improved accuracy and efficiency in HVAC design, reduced energy consumption and operating costs, enhanced project collaboration and documentation, and compliance with industry standards and regulations.
How does HVAC software assist in equipment selection and sizing?
HVAC software utilizes load calculations to determine the appropriate capacity and efficiency requirements for HVAC equipment. It integrates with manufacturers’ databases to provide a comprehensive selection of options, ensuring optimal equipment selection and sizing for each project.
What types of load calculations can HVAC software perform?
HVAC software can perform various types of load calculations, including heating load calculations to determine the heat loss of a building and cooling load calculations to determine the cooling load. These calculations consider factors such as building dimensions, climate data, and occupancy patterns.