In today’s modern buildings, efficient and intelligent HVAC systems are essential for maintaining optimal indoor environments while minimizing energy consumption. HVAC software that seamlessly integrates with building automation systems (BAS) plays a crucial role in achieving these goals, offering a comprehensive solution for enhanced building management and occupant comfort.
With advanced data analytics, control capabilities, and user-friendly interfaces, HVAC software empowers facility managers and operators to optimize system performance, reduce operating costs, and ensure occupant well-being. By bridging the gap between HVAC systems and BAS, this software unlocks a new level of building intelligence, enabling data-driven decision-making and proactive maintenance.
Integration Capabilities
HVAC software seamlessly integrates with building automation systems (BAS), enabling centralized control and monitoring of all HVAC equipment. Integration occurs through open protocols like BACnet, Modbus, and OPC, ensuring compatibility with various BAS platforms.For instance, integrating HVAC software with a BAS allows for real-time monitoring of equipment performance, energy consumption, and indoor environmental conditions.
This data can be analyzed to optimize HVAC operations, reduce energy costs, and enhance occupant comfort.
Open Protocols and Standards
Open protocols and standards play a crucial role in effective HVAC software integration. They ensure seamless communication between different devices and systems, regardless of manufacturer or model. BACnet, Modbus, and OPC are widely adopted open protocols that facilitate data exchange and interoperability between HVAC software and BAS.By
adhering to open standards, HVAC software can easily integrate with existing BAS, eliminating the need for custom interfaces or proprietary protocols. This simplifies installation, reduces integration costs, and ensures long-term compatibility with evolving BAS technologies.
Data Management and Analytics
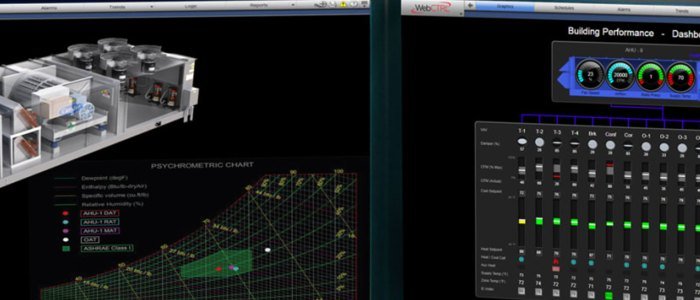
HVAC software is equipped with advanced data management and analytics capabilities that allow it to collect, store, and analyze vast amounts of data from building automation systems. This data includes temperature, humidity, airflow, energy consumption, and other critical parameters that provide valuable insights into the performance of the HVAC system.
By leveraging data analytics, HVAC software can identify trends, patterns, and inefficiencies in the system. This information can then be used to optimize HVAC performance, reduce energy consumption, and improve overall building comfort.
Dashboards and Reporting Tools
HVAC software often includes customizable dashboards and reporting tools that allow users to easily visualize and interpret data insights. These dashboards can be tailored to specific user roles and needs, providing a comprehensive overview of system performance, energy usage, and maintenance requirements.
Reports generated by the software can provide detailed breakdowns of energy consumption, equipment performance, and system efficiency. This information can be used to identify areas for improvement, justify energy-saving initiatives, and demonstrate the return on investment for HVAC upgrades.
Control and Optimization

HVAC software can control and optimize HVAC systems based on data from building automation systems. This enables efficient and comfortable building environments while reducing energy consumption.
Specific control strategies include:
- Demand-controlled ventilation: adjusts ventilation rates based on occupancy and air quality.
- Optimal start/stop: optimizes equipment operation to minimize energy waste during unoccupied periods.
- Fault detection and diagnostics: identifies and resolves system issues proactively, preventing breakdowns.
Machine learning and artificial intelligence are also used to enhance HVAC control:
- Predictive analytics: forecasts energy demand and occupant behavior, enabling proactive system adjustments.
- Adaptive control: adjusts system parameters in real-time based on changing conditions, improving energy efficiency and comfort.
User Interface and Accessibility
The user interface of HVAC software plays a crucial role in facilitating effective interaction with building automation systems. It should be designed with an intuitive and user-friendly approach to enable seamless control and monitoring for operators and facility managers.
An intuitive design allows users to navigate the software effortlessly, accessing essential functions and data with minimal effort. Easy-to-understand menus, graphical representations, and customizable dashboards enhance the user experience, empowering operators to make informed decisions and respond promptly to system changes.
Mobile Apps and Remote Access
In today’s fast-paced environment, mobile apps and remote access capabilities have become indispensable for HVAC software. These features provide facility managers and operators with the flexibility to monitor and control systems remotely, ensuring uninterrupted operation and timely responses to any issues.
- Mobile apps allow users to access real-time data, adjust settings, and receive notifications from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Remote access enables authorized personnel to connect to the HVAC system remotely, troubleshoot issues, and make necessary adjustments without being physically present at the facility.
These mobile and remote access capabilities enhance operational efficiency, improve response times, and provide peace of mind to facility managers.
Security and Compliance
HVAC software incorporates robust security measures to safeguard sensitive data and protect systems from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Compliance with industry standards and regulations ensures the software meets the highest security benchmarks.
Data Protection and Privacy
HVAC software employs encryption algorithms, access control mechanisms, and intrusion detection systems to protect data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Data encryption ensures that unauthorized individuals cannot access or interpret sensitive information, such as building temperature settings, occupancy data, and energy consumption patterns.
Industry Standards and Compliance
HVAC software adheres to industry standards and regulations, such as ASHRAE Guideline 13 and ISO 27001. These standards provide a framework for implementing secure and compliant HVAC systems, ensuring that software meets the required security protocols and best practices.
Cybersecurity and Protection
HVAC systems are vulnerable to cyberattacks, including malware, phishing, and unauthorized access. HVAC software incorporates cybersecurity features to protect against these threats. Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular software updates help prevent unauthorized access, detect suspicious activity, and mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Case Studies and Implementation
Integrating HVAC software with building automation systems has proven to enhance energy efficiency, improve occupant comfort, and streamline operations in various building types. Here are case studies and insights to help you understand the implementation process and its benefits.
Successful HVAC software implementations require careful planning, collaboration, and adherence to best practices. Common challenges include data compatibility, system integration, and user adoption. Overcoming these challenges involves thorough system testing, comprehensive training, and ongoing support.
Case Study: Commercial Office Building
In a 20-story commercial office building, HVAC software integration led to a 20% reduction in energy consumption. The software optimized HVAC operations based on real-time occupancy and weather data, reducing unnecessary heating and cooling.
Case Study: Healthcare Facility
A hospital implemented HVAC software to improve patient comfort and reduce the risk of infection. The software provided real-time monitoring of air quality, temperature, and humidity, allowing for prompt adjustments to ensure optimal conditions for patients and staff.
Case Study: Educational Institution
A university integrated HVAC software with its building automation system to enhance energy efficiency and provide a comfortable learning environment. The software automated HVAC operations based on class schedules and occupancy data, reducing energy waste during unoccupied hours.
Best Practices for Effective Implementation
- Define clear goals and objectives for the implementation.
- Engage stakeholders, including building owners, facility managers, and occupants, throughout the process.
- Conduct thorough system testing and validation before going live.
- Provide comprehensive training to users to ensure proper operation and maintenance.
- Monitor and evaluate system performance regularly to identify areas for improvement.
Lessons Learned
- Data compatibility issues can arise due to different software and hardware platforms. Ensure compatibility before implementation.
- System integration requires careful coordination between HVAC contractors, software vendors, and building automation system providers.
- User adoption is crucial for successful implementation. Engage users early on and address their concerns and feedback.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, HVAC software that integrates with building automation systems is a transformative technology that empowers facility managers and operators to elevate building performance to new heights. By seamlessly connecting HVAC systems with BAS, this software provides a comprehensive solution for optimizing energy efficiency, enhancing occupant comfort, and ensuring the smooth operation of modern buildings.
As the industry continues to evolve, the integration of HVAC software and BAS will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of building management innovation.
Common Queries
What are the key benefits of integrating HVAC software with building automation systems?
Integrating HVAC software with BAS offers numerous benefits, including enhanced energy efficiency, improved occupant comfort, reduced maintenance costs, and streamlined operations.
How does HVAC software collect and analyze data from building automation systems?
HVAC software utilizes various sensors and data points within the BAS to collect real-time data on system performance, energy consumption, and indoor environmental conditions. This data is then analyzed to identify trends, optimize settings, and generate actionable insights.
What role does user interface play in HVAC software integration with building automation systems?
An intuitive and user-friendly interface is crucial for effective integration between HVAC software and BAS. It enables facility managers and operators to easily monitor system performance, adjust settings, and access data insights, ensuring seamless operation and efficient building management.
How does HVAC software contribute to improved security and compliance in building automation systems?
HVAC software often incorporates robust security measures to protect data and systems from unauthorized access and cyberattacks. Compliance with industry standards and regulations, such as ASHRAE and ISO, is also ensured, providing peace of mind and minimizing potential risks.