In the realm of modern HVAC systems, software has emerged as a game-changer, providing unparalleled capabilities for optimizing performance, reducing energy consumption, and ensuring occupant comfort. HVAC software that generates reports and insights empowers facility managers and building owners with the data-driven intelligence they need to make informed decisions, maximize efficiency, and proactively address potential issues.
With advanced features and functionalities, HVAC software empowers users to collect, analyze, and visualize data from sensors and other sources, providing a comprehensive understanding of system performance. This data-driven approach enables users to identify trends, pinpoint inefficiencies, and make proactive adjustments to optimize energy usage, improve indoor air quality, and enhance overall system reliability.
Software Capabilities
HVAC software that generates reports and insights provides a range of features and functionalities to assist in optimizing HVAC systems. These software tools enable users to analyze system performance, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions to enhance efficiency and comfort.
Key features of HVAC reporting and insights software include:
- Data collection and analysis: Software collects data from sensors and meters installed throughout the HVAC system, including temperature, humidity, airflow, and energy consumption.
- Reporting and visualization: Software generates customizable reports and dashboards that present data in a clear and concise manner, allowing users to easily identify trends and patterns.
- Fault detection and diagnostics: Software monitors system performance and identifies potential faults or inefficiencies, enabling proactive maintenance and repairs.
- Energy efficiency optimization: Software analyzes energy consumption data and provides recommendations for improvements, such as adjusting set points, optimizing equipment operation, and implementing energy-saving measures.
- Comfort optimization: Software considers factors such as temperature, humidity, and airflow to ensure optimal occupant comfort and satisfaction.
Specific Software Tools and Functionalities
Various HVAC reporting and insights software tools are available, each with its own unique set of features and functionalities. Some popular examples include:
- EnergyCAP: Comprehensive energy management software that includes HVAC reporting and analysis capabilities.
- SkySpark: Cloud-based HVAC monitoring and analytics platform that provides real-time data and insights.
- Veris Industries: Software suite that offers a range of HVAC monitoring and reporting tools, including fault detection and energy optimization.
Types of Reports and Insights
HVAC software can generate a wide range of reports and insights that can help you optimize your HVAC system and make informed decisions.
These reports can be customized to meet your specific needs, and they can provide valuable information on:
- Energy consumption
- Equipment performance
- Maintenance needs
- System efficiency
By using these reports, you can identify areas where you can improve your HVAC system’s performance and save money.
Customizable Reports
HVAC software allows you to customize reports to meet your specific needs. You can choose the data you want to include in the report, as well as the format of the report.
This flexibility makes it easy to get the information you need in the format that you want.
Benefits of Using Reports for Decision-Making
The reports and insights generated by HVAC software can be a valuable tool for decision-making.
- By understanding your HVAC system’s performance, you can make informed decisions about how to improve it.
- You can also use the reports to identify areas where you can save money on energy costs.
Overall, HVAC software can provide you with the information you need to make informed decisions about your HVAC system.
Data Collection and Analysis
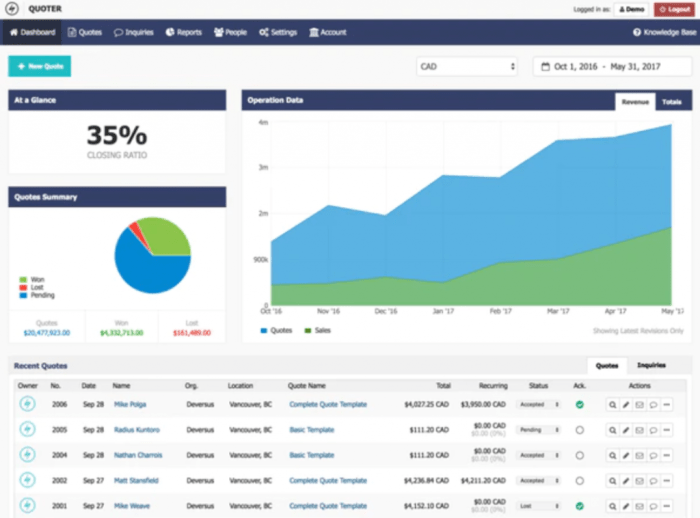
HVAC software collects data from sensors installed in the HVAC system, such as temperature, humidity, airflow, and energy consumption. The data is collected and stored in a database, where it can be analyzed to identify trends and patterns.
The software uses various methods to analyze the data, including:
- Statistical analysis: This method uses statistical techniques to identify trends and patterns in the data. For example, the software can use statistical analysis to identify the average temperature of a room over time.
- Machine learning: This method uses machine learning algorithms to identify patterns in the data that are not easily detectable by humans. For example, the software can use machine learning to identify the relationship between the temperature of a room and the energy consumption of the HVAC system.
The data analysis can be used to generate insights that can help to improve HVAC system performance. For example, the software can use the data to:
- Identify areas where the HVAC system is wasting energy.
- Predict future energy consumption.
- Optimize the operation of the HVAC system to reduce energy consumption.
User Interface and Accessibility
The user interface of HVAC software is designed to be intuitive and easy to use. The software is organized into a series of menus and toolbars that provide quick access to all of the software’s features. The user interface is also customizable, so users can tailor the software to their own specific needs.Accessibility
is an important consideration for any software product, and HVAC software is no exception. The software is compatible with a variety of platforms, including Windows, Mac, and Linux. The software is also available in a variety of languages, making it accessible to users around the world.User-friendly
software enhances the user experience by making it easy for users to find the information they need and complete their tasks quickly and efficiently. HVAC software is designed to be user-friendly, with a clear and concise user interface that makes it easy for users to navigate the software and find the information they need.
Intuitive Interface
The user interface of HVAC software is designed to be intuitive and easy to use. The software is organized into a series of menus and toolbars that provide quick access to all of the software’s features. The user interface is also customizable, so users can tailor the software to their own specific needs.
Accessibility and Compatibility
HVAC software is compatible with a variety of platforms, including Windows, Mac, and Linux. The software is also available in a variety of languages, making it accessible to users around the world.
Enhanced User Experience
User-friendly software enhances the user experience by making it easy for users to find the information they need and complete their tasks quickly and efficiently. HVAC software is designed to be user-friendly, with a clear and concise user interface that makes it easy for users to navigate the software and find the information they need.
Integration with Other Systems
HVAC software offers seamless integration with various building management systems, enabling comprehensive data analysis and control. This integration streamlines operations, optimizes energy consumption, and enhances overall building performance.
By connecting HVAC software to other systems, such as building automation systems (BAS), energy management systems (EMS), and lighting control systems, facilities managers gain a holistic view of building operations. This allows for:
Data Consolidation
- Centralized collection and analysis of data from multiple sources, providing a comprehensive overview of building performance.
- Elimination of data silos, ensuring that all relevant information is accessible in a single platform.
Automated Control
- Automated adjustments to HVAC settings based on real-time data from integrated systems, optimizing energy efficiency and occupant comfort.
- Reduced manual intervention, freeing up facilities managers to focus on strategic tasks.
Improved Decision-Making
- Access to consolidated data and insights enables data-driven decision-making, leading to improved system performance and reduced operating costs.
- Historical data analysis helps identify trends and patterns, facilitating predictive maintenance and proactive problem-solving.
For example, integrating HVAC software with a BAS allows for real-time monitoring and control of HVAC equipment, lighting, and other building systems. This enables facilities managers to optimize temperature, ventilation, and lighting levels based on occupancy and environmental conditions, resulting in significant energy savings and improved occupant comfort.
Security and Data Protection
HVAC software prioritizes data security and protection to safeguard sensitive information. It employs robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber threats.
Compliance with Industry Standards
HVAC software adheres to industry-recognized security standards, such as ISO 27001 and NIST Cybersecurity Framework, ensuring compliance with best practices for data protection.
Data Encryption
Sensitive data, including HVAC system configurations, energy consumption data, and user information, is encrypted at rest and in transit using industry-standard encryption algorithms like AES-256. This encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption key.
Role-Based Access Control
HVAC software implements role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles and permissions. This prevents unauthorized users from accessing or modifying critical information.
Regular Security Updates
HVAC software providers regularly release security updates and patches to address potential vulnerabilities and enhance the software’s overall security posture.
Robust Security Enhances HVAC System Reliability
Robust security measures in HVAC software contribute to the reliability of HVAC systems by:
- Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access, preventing disruptions to HVAC operations.
- Preventing malicious attacks that could compromise HVAC system functionality, ensuring optimal performance.
- Maintaining data integrity and accuracy, ensuring that HVAC systems operate based on reliable and trustworthy information.
Last Word
In conclusion, HVAC software that generates reports and insights is an indispensable tool for facility managers and building owners seeking to optimize system performance, reduce energy consumption, and ensure occupant comfort. By leveraging data-driven insights, these software solutions empower users to make informed decisions, proactively address potential issues, and achieve a new level of efficiency and control over their HVAC systems.
Q&A
How does HVAC software generate reports and insights?
HVAC software collects data from sensors and other sources, analyzes the data using advanced algorithms, and generates customized reports and insights tailored to specific user needs.
What types of reports and insights can HVAC software provide?
HVAC software can generate a wide range of reports and insights, including energy consumption reports, equipment performance reports, maintenance schedules, and predictive analytics.
How can HVAC software help optimize HVAC systems?
HVAC software provides data-driven insights that enable users to identify inefficiencies, optimize energy usage, improve indoor air quality, and extend equipment life.
Is HVAC software easy to use?
Yes, HVAC software is typically designed with user-friendly interfaces and intuitive navigation, making it accessible to users with varying levels of technical expertise.
How does HVAC software integrate with other systems?
HVAC software often offers integration capabilities with other building management systems, enabling seamless data exchange and comprehensive control over building operations.