In the dynamic realm of engineering, HVAC systems play a pivotal role in ensuring thermal comfort and energy efficiency. To navigate the complexities of these systems, engineers rely on specialized software tools that empower them to design, analyze, and optimize HVAC solutions.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of HVAC software, exploring its capabilities, key features, and the latest trends shaping its evolution.
HVAC software serves as an indispensable tool for engineers, streamlining their workflows and enabling them to tackle complex design challenges with precision and efficiency. From conceptualizing HVAC systems to simulating their performance, these software solutions empower engineers to deliver optimal solutions that meet the unique demands of every project.
Introduction
HVAC software, or Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning software, is a specialized tool designed to assist engineers in designing, analyzing, and optimizing HVAC systems. It provides a comprehensive suite of features that enable engineers to perform complex calculations, create detailed models, and generate accurate reports.The
use of HVAC software offers numerous benefits for engineers. It streamlines the design process, reduces errors, and improves the efficiency of HVAC systems. Engineers can leverage the software to quickly generate accurate load calculations, select appropriate equipment, and simulate system performance under various operating conditions.
By automating repetitive tasks and providing real-time feedback, HVAC software empowers engineers to make informed decisions and deliver optimal HVAC solutions.
Benefits of Using HVAC Software for Engineers
-
-*Enhanced Accuracy and Reliability
HVAC software utilizes advanced algorithms and industry-accepted standards to ensure accurate calculations and reliable results. It eliminates the risk of manual errors and provides engineers with confidence in their designs.
-*Time-Saving and Efficiency
By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining the design process, HVAC software significantly reduces the time required to complete projects. Engineers can focus on higher-level design aspects and optimize their workflow.
-*Optimized System Performance
HVAC software allows engineers to simulate system performance under various operating conditions. This enables them to identify and address potential issues early on, ensuring optimal system efficiency and occupant comfort.
-*Improved Collaboration and Communication
HVAC software facilitates seamless collaboration between engineers and other stakeholders. It provides a central platform for sharing designs, reviewing results, and generating reports, fostering effective communication and coordination.
-*Enhanced Sustainability
HVAC software incorporates sustainability features that help engineers design energy-efficient systems. It provides insights into energy consumption, carbon footprint, and indoor air quality, enabling engineers to make informed decisions that promote environmental sustainability.
Key Features of HVAC Software
HVAC software is a valuable tool for engineers to design, analyze, and optimize HVAC systems.
To select the right software, it is important to understand the key features that are available.
Some of the essential features that HVAC software should possess include:
- Load calculations: Software should be able to perform accurate load calculations for heating, cooling, and ventilation systems.
- System design: Software should provide tools for designing HVAC systems, including ductwork, piping, and equipment selection.
- Energy analysis: Software should be able to analyze the energy consumption of HVAC systems and identify opportunities for improvement.
- Control integration: Software should be able to integrate with building automation systems to control HVAC equipment and optimize performance.
The advantages of using HVAC software include:
- Improved accuracy: Software can help engineers to perform more accurate calculations and designs.
- Increased efficiency: Software can help engineers to design more efficient HVAC systems that consume less energy.
- Reduced costs: Software can help engineers to reduce the cost of HVAC systems by identifying opportunities for optimization.
However, there are also some disadvantages to using HVAC software:
- Cost: HVAC software can be expensive to purchase and maintain.
- Complexity: HVAC software can be complex to use, especially for engineers who are not familiar with the software.
- Accuracy: The accuracy of HVAC software depends on the quality of the input data.
Some examples of specific HVAC software that offers these features include:
- Carrier HAP: Carrier HAP is a comprehensive HVAC software suite that includes load calculations, system design, energy analysis, and control integration.
- Trane Trace: Trane Trace is a powerful HVAC software tool that provides engineers with the ability to design, analyze, and optimize HVAC systems.
- Revit MEP: Revit MEP is a BIM (Building Information Modeling) software that includes tools for designing and analyzing HVAC systems.
Types of HVAC Software
HVAC software is categorized based on its functionality and applications. Each type has unique characteristics and uses, catering to specific needs in HVAC system design and analysis.
Types of HVAC Software
- Load Calculation Software: Determines the heating and cooling loads of a building, considering factors like building envelope, occupancy, and climate data.
- System Design Software: Assists in designing and selecting HVAC systems, including equipment sizing, ductwork layout, and control strategies.
- Energy Modeling Software: Simulates the energy performance of HVAC systems, evaluating energy consumption and identifying opportunities for optimization.
- CFD Software: Uses computational fluid dynamics to analyze airflow patterns, temperature distribution, and indoor air quality within a building.
- Control System Software: Configures and programs HVAC control systems, ensuring efficient operation and maintaining desired indoor conditions.
- Commissioning Software: Supports the commissioning process, verifying system performance and ensuring it meets design specifications.
Selection Criteria for HVAC Software
Choosing the right HVAC software is crucial for efficient and effective HVAC system design and analysis. To make an informed decision, it is essential to consider key factors and evaluate software based on specific requirements.
Here are some important selection criteria to consider:
Key Factors to Consider
- Project complexity: Determine the complexity of the HVAC systems you will be working on. Some software is designed for simple systems, while others can handle complex projects with multiple zones and advanced features.
- System types: Identify the types of HVAC systems you will be designing, such as air handling units, chillers, boilers, and variable air volume (VAV) systems. Ensure the software supports the system types you need.
- User interface: Consider the user interface of the software. It should be intuitive, easy to navigate, and customizable to your workflow.
- Interoperability: Determine if the software can integrate with other design and analysis tools you use, such as CAD software or building information modeling (BIM) software.
- Support and documentation: Ensure the software vendor provides adequate technical support and comprehensive documentation to help you troubleshoot issues and maximize software functionality.
Importance of Evaluating Software Based on Specific Requirements
It is crucial to evaluate HVAC software based on your specific requirements. Each project has unique needs, and different software may be better suited for different applications. Consider the following:
- Functional requirements: Determine the specific features and capabilities you need from the software, such as load calculations, system sizing, and energy analysis.
- Budget: Establish a budget for the software and consider the licensing costs, maintenance fees, and training expenses.
- Timeline: Consider the timeline for your project and choose software that can meet your deadlines.
Decision Matrix for HVAC Software Selection
To assist in the selection process, you can create a decision matrix that compares different software options based on your evaluation criteria. This matrix will help you visualize the strengths and weaknesses of each software and make an informed decision.
5. Implementation and Integration
Implementing and integrating HVAC software involves several crucial steps that determine the success of the project. Understanding these steps and adhering to best practices can streamline the process and maximize the software’s benefits.
The implementation process typically begins with gathering requirements from stakeholders, including engineers, technicians, and facility managers. These requirements should align with the organization’s specific needs and objectives for the software.
System Configuration
Once the requirements are defined, the software is configured to meet those specifications. This involves setting up system parameters, defining control strategies, and integrating with existing building automation systems (BAS) or other software applications.
Training and Support
Thorough training for users is essential to ensure they can effectively utilize the software’s features and functionality. Comprehensive documentation and ongoing support from the software vendor are crucial for smooth implementation and continued success.
Data Collection and Analysis
HVAC software often collects and analyzes data from sensors and other sources to provide insights into system performance. This data can be used to optimize energy consumption, improve occupant comfort, and identify potential issues before they escalate.
Challenges and Best Practices
Common challenges during HVAC software implementation include data compatibility issues, integration difficulties, and user resistance to change. To overcome these challenges, it is recommended to involve all stakeholders in the planning and implementation process, ensure compatibility between the software and existing systems, and provide ample training and support.
Case Studies
Successful HVAC software implementations have been reported in various industries and applications. For instance, a university campus implemented an integrated HVAC solution that resulted in significant energy savings and improved occupant comfort. Another example is a healthcare facility that utilized HVAC software to optimize airflow and reduce the risk of airborne infections.
Training and Support
Thorough training and continuous support are crucial for effective utilization of HVAC software. Users must be equipped with the knowledge and skills to navigate the software’s features and functions efficiently.
Various training options are available, including online tutorials, webinars, workshops, and on-site training. The choice of training method depends on the user’s learning style, schedule, and budget.
Online Tutorials and Webinars
- Self-paced and convenient, allowing users to learn at their own pace.
- Often free or low-cost, making them accessible to a wide audience.
- Limited interactivity and may not provide personalized guidance.
Workshops and On-Site Training
- Interactive and hands-on, enabling users to practice and ask questions.
- Typically more expensive than online options but provide personalized instruction.
- Can be tailored to specific project requirements and user skill levels.
Ongoing Support
Beyond initial training, ongoing support is essential to ensure users can resolve issues and maximize the software’s potential. This support can be provided through:
- Online forums and knowledge bases
- Technical support hotlines
- Software updates and patches
Effective training and support strategies involve:
- Identifying user needs and tailoring training accordingly.
- Providing ongoing support to address user queries and resolve issues.
- Encouraging user feedback to improve training and support materials.
Future Trends in HVAC Software
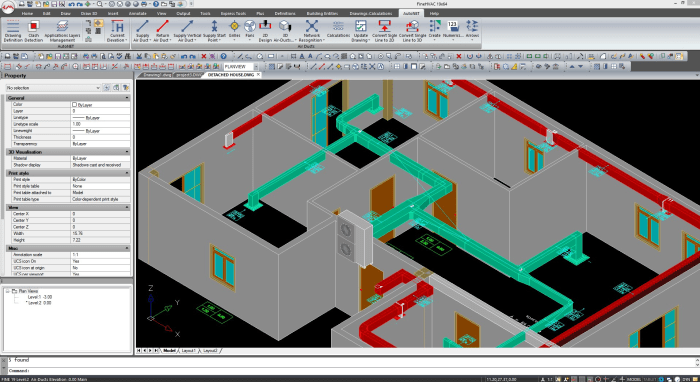
The HVAC industry is constantly evolving, and so is the software that engineers use to design and manage HVAC systems. In recent years, we have seen a number of emerging trends in HVAC software technology, including:
- Cloud-based software: Cloud-based HVAC software is becoming increasingly popular because it offers a number of advantages over traditional on-premises software. Cloud-based software is accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, which makes it ideal for engineers who work remotely or who need to access their software from multiple locations.
- Building information modeling (BIM): BIM is a process for creating and managing digital representations of buildings. BIM software can be used to create detailed models of HVAC systems, which can help engineers to design and manage systems more efficiently.
- Artificial intelligence (AI): AI is being used to develop new HVAC software features that can help engineers to design and manage systems more efficiently. For example, AI can be used to optimize system performance, identify potential problems, and generate reports.
These trends are having a significant impact on the future of HVAC engineering. Cloud-based software is making it easier for engineers to collaborate on projects and access their software from anywhere. BIM is helping engineers to design and manage systems more efficiently.
And AI is helping engineers to optimize system performance and identify potential problems.
As these trends continue to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and powerful HVAC software tools in the future. These tools will help engineers to design and manage HVAC systems more efficiently and effectively, which will lead to better building performance and lower energy costs.
Emerging Technologies and Advancements
In addition to the trends discussed above, there are a number of other emerging technologies and advancements that are expected to have a significant impact on the future of HVAC software. These include:
- Virtual reality (VR): VR is being used to create immersive training experiences for HVAC engineers. VR can be used to simulate real-world scenarios, which can help engineers to learn how to operate and maintain HVAC systems more effectively.
- Augmented reality (AR): AR is being used to develop new HVAC software tools that can help engineers to visualize and interact with HVAC systems in the real world. AR can be used to overlay digital information onto the real world, which can help engineers to identify potential problems and make repairs more quickly and efficiently.
- Blockchain: Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that is being used to develop new HVAC software tools that can help to improve the security and transparency of HVAC systems. Blockchain can be used to track the history of HVAC systems, which can help to identify potential problems and improve maintenance.
These emerging technologies and advancements are still in their early stages of development, but they have the potential to revolutionize the way that HVAC engineers design and manage HVAC systems. As these technologies continue to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and powerful HVAC software tools in the future.
Final Thoughts
As the future of HVAC engineering unfolds, software will continue to play an increasingly pivotal role. With the advent of cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning, HVAC software is poised to transform the way engineers design, analyze, and operate HVAC systems.
By embracing these advancements, engineers can unlock new possibilities and drive the industry towards a more sustainable and efficient future.
FAQ Corner
What are the core benefits of using HVAC software for engineers?
HVAC software offers a myriad of benefits for engineers, including improved design accuracy, reduced project timelines, enhanced energy efficiency, and streamlined collaboration.
How do I choose the right HVAC software for my needs?
Selecting the optimal HVAC software involves evaluating factors such as the specific project requirements, the desired features, the level of technical support, and the software’s compatibility with existing systems.
What are some emerging trends in HVAC software technology?
The future of HVAC software is marked by advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing, enabling engineers to automate tasks, optimize system performance, and access data from anywhere.