In the realm of energy conservation, HVAC software has emerged as an indispensable tool for optimizing building performance. By leveraging advanced algorithms and sophisticated simulations, this software empowers engineers, architects, and facility managers to make informed decisions that enhance energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
HVAC software for energy modeling provides a comprehensive platform for simulating and analyzing the thermal and energy behavior of buildings. This allows professionals to evaluate various design options, equipment selections, and operational strategies to identify the most energy-efficient solutions. By harnessing the power of these software tools, we can create more sustainable and cost-effective buildings that contribute to a greener future.
Overview of HVAC Software for Energy Modeling
HVAC software for energy modeling is a specialized tool that enables engineers, architects, and other professionals to simulate and analyze the energy performance of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems in buildings.
This software provides detailed insights into energy consumption patterns, system efficiency, and overall building performance, allowing designers to make informed decisions during the design and operation stages of a building’s lifecycle.
Benefits of Using HVAC Software for Energy Modeling
- Improved Energy Efficiency: HVAC software helps identify inefficiencies in system design and operation, enabling engineers to optimize settings and configurations for maximum energy savings.
- Reduced Operating Costs: By identifying and addressing energy inefficiencies, HVAC software can significantly reduce operating costs associated with heating, cooling, and ventilation.
- Enhanced Comfort Levels: HVAC software allows designers to simulate and optimize system performance to ensure optimal comfort levels for building occupants.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many countries have regulations regarding energy efficiency in buildings. HVAC software helps ensure compliance with these regulations by providing accurate energy consumption data.
- Informed Decision-Making: HVAC software provides engineers and architects with detailed information to make informed decisions about system design, equipment selection, and operational strategies.
Types of HVAC Software for Energy Modeling
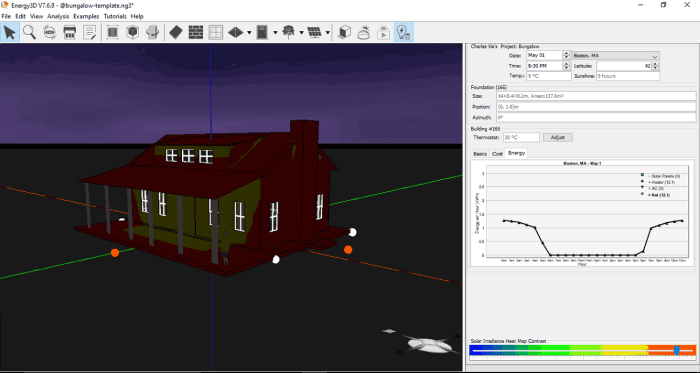
HVAC software for energy modeling can be categorized into several types, each with distinct capabilities and limitations. The choice of software depends on the specific requirements of the project and the expertise of the user.
Simulation-Based Software
Simulation-based software uses mathematical models to simulate the behavior of an HVAC system over time. These models account for various factors, such as heat transfer, fluid flow, and equipment performance. Simulation-based software provides detailed results and can be used to optimize system design and operation.
Capabilities:
- Detailed modeling of HVAC systems
- Prediction of system performance under various conditions
- Optimization of system design and operation
Limitations:
- Requires extensive input data and expertise
- Can be computationally intensive and time-consuming
- May not be suitable for all project types
Rule-Based Software
Rule-based software uses a set of pre-defined rules to estimate energy consumption. These rules are based on empirical data and industry standards. Rule-based software is relatively easy to use and requires less input data than simulation-based software.
Capabilities:
- Quick and easy to use
- Requires minimal input data
- Suitable for preliminary energy modeling
Limitations:
- Less accurate than simulation-based software
- Not suitable for complex or customized systems
- May not be compliant with all energy codes
Data-Driven Software
Data-driven software uses historical data to predict future energy consumption. This data can be collected from building automation systems, utility bills, or other sources. Data-driven software is often used for benchmarking and tracking energy performance over time.
Capabilities:
- Leverages historical data for accurate predictions
- Provides insights into energy consumption patterns
- Can be used for ongoing performance monitoring
Limitations:
- Requires access to reliable historical data
- May not be suitable for predicting performance under new conditions
- Can be complex to implement and maintain
3. Key Features of HVAC Software for Energy Modeling
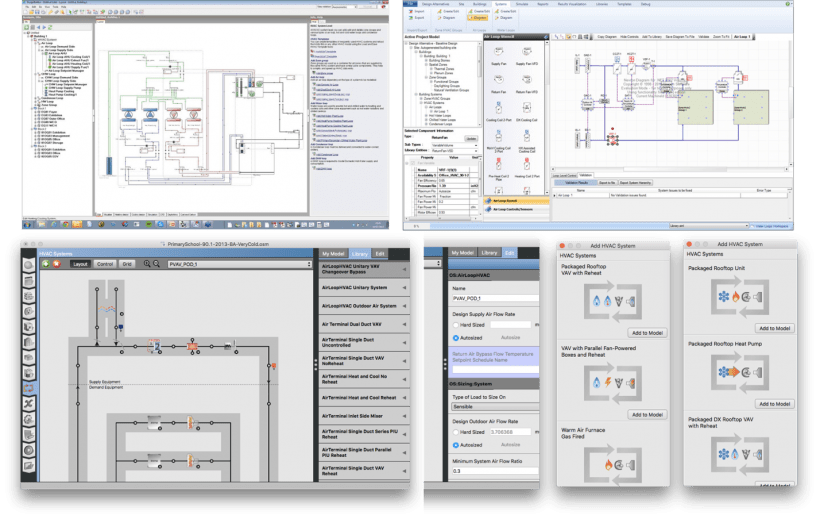
Selecting the right HVAC software for energy modeling requires careful consideration of essential features that enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and usability of the software.
Here are the key features to look for and their importance:
User Interface
- An intuitive and user-friendly interface simplifies the learning curve and allows users to navigate the software seamlessly.
- Customizable dashboards provide quick access to frequently used features and project-specific data.
- Drag-and-drop functionality enables efficient model creation and modification.
Energy Simulation Engine
- Accurate and robust simulation engine ensures reliable energy consumption predictions.
- Ability to handle complex building models and HVAC systems.
- Compliance with industry standards and building codes.
Load Calculations
- Comprehensive load calculations for heating, cooling, and ventilation.
- Consideration of building envelope, internal heat gains, and occupancy patterns.
- Integration with other design tools for accurate load estimation.
Equipment Modeling
- Extensive library of HVAC equipment models, including chillers, boilers, and air handlers.
- Ability to create custom equipment models for specialized systems.
- Accurate performance data for equipment selection and optimization.
Reporting and Analysis
- Comprehensive reporting capabilities for energy consumption, cost analysis, and environmental impact.
- Customization of reports for specific project requirements.
- Advanced data visualization tools for easy interpretation of results.
Integration and Interoperability
- Integration with other building design software for seamless workflow.
- Support for industry-standard file formats for data exchange.
- Cloud-based collaboration tools for efficient team coordination.
Technical Support and Documentation
- Responsive technical support team for assistance and troubleshooting.
- Comprehensive user manuals and training materials for effective software utilization.
- Regular software updates and enhancements for improved functionality.
4. Applications of HVAC Software for Energy Modeling
HVAC software is extensively used in energy modeling to enhance the design and operation of HVAC systems. It provides accurate predictions of energy consumption, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact, enabling engineers and architects to make informed decisions.
The applications of HVAC software in energy modeling are diverse, including:
Building Design and Optimization
- Predicting the energy consumption of proposed HVAC systems during the design phase.
- Evaluating the impact of different HVAC design options on energy efficiency and cost.
- Optimizing HVAC system performance by simulating various operating conditions.
Energy Audits and Retrofits
- Analyzing existing HVAC systems to identify areas for energy savings.
- Developing energy-saving retrofit measures and evaluating their potential benefits.
- Verifying the energy savings achieved after implementing retrofit measures.
Energy Code Compliance
- Ensuring that new and existing HVAC systems comply with energy codes and standards.
- Providing documentation to support compliance with energy code requirements.
- Identifying opportunities for exceeding energy code requirements and achieving higher energy efficiency.
Benefits and Outcomes of Using HVAC Software in Energy Modeling
- Improved energy efficiency, leading to reduced energy consumption and operating costs.
- Optimized HVAC system performance, resulting in enhanced comfort levels and indoor air quality.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to environmental sustainability.
- Increased compliance with energy codes and standards, ensuring regulatory compliance and potential incentives.
- Enhanced decision-making, enabling engineers and architects to make informed choices based on accurate data and analysis.
Selection and Implementation of HVAC Software for Energy Modeling
Selecting and implementing HVAC software for energy modeling is a crucial step in optimizing energy efficiency and reducing operating costs in buildings. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the selection and implementation process to help you make informed decisions and ensure a successful implementation.
The process involves evaluating your specific needs, researching available software options, and carefully planning the implementation to ensure seamless integration with your existing systems and workflows.
Factors to Consider in Selecting HVAC Software
- Building Type and Complexity: Different software programs are tailored to specific building types, such as residential, commercial, or industrial, and can handle varying levels of complexity.
- Energy Modeling Objectives: Determine the specific goals you aim to achieve with energy modeling, such as compliance with regulations, reducing energy consumption, or optimizing system performance.
- User Interface and Usability: The software should be user-friendly and intuitive to navigate, with clear documentation and support resources available.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Consider the compatibility of the software with your existing HVAC systems, building management systems, and other software applications.
- Cost and Budget: Determine the software’s licensing fees, maintenance costs, and any additional expenses associated with implementation and training.
Steps in Implementing HVAC Software
- Software Selection: Conduct thorough research, evaluate software options based on your selection criteria, and select the software that best meets your needs.
- Installation and Configuration: Install the software on the designated computers and configure it to meet your specific requirements and building parameters.
- Model Creation and Validation: Create a detailed energy model of your building, including HVAC systems, building envelope, and occupant behavior. Validate the model to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Energy Analysis and Optimization: Use the software to perform energy simulations, analyze results, and identify opportunities for energy efficiency improvements.
- Training and Support: Provide training to users on how to operate the software effectively and access technical support as needed to ensure ongoing success.
Case Studies and Best Practices
Case studies and best practices showcase the successful application of HVAC software for energy modeling, providing valuable insights into its effectiveness. By examining real-world examples, we can learn from the experiences of others and identify strategies for optimizing energy efficiency.
One notable case study involves a commercial building in California that used HVAC software to analyze its energy consumption. The software identified inefficiencies in the HVAC system, leading to the implementation of targeted upgrades. These upgrades resulted in a significant reduction in energy usage, reducing operating costs and environmental impact.
Best Practices
To ensure effective use of HVAC software for energy modeling, it is crucial to follow best practices. These include:
- Defining clear project goals and objectives.
- Gathering accurate building data and input parameters.
- Selecting the appropriate software tool for the specific project requirements.
- Calibrating the model to ensure accuracy.
- Interpreting the results carefully and identifying opportunities for improvement.
Future Trends in HVAC Software for Energy Modeling
The future of HVAC software for energy modeling is promising, with several emerging trends poised to impact the industry.
One notable trend is the increasing adoption of cloud-based software, which offers several advantages such as scalability, accessibility, and reduced hardware requirements. This shift towards cloud-based solutions allows for easier collaboration and data sharing among project stakeholders.
Data Analytics and Machine Learning
Another trend is the integration of data analytics and machine learning into HVAC software. These technologies enable the analysis of large amounts of data to identify patterns, optimize system performance, and predict future energy consumption. By leveraging data-driven insights, engineers can make more informed decisions and improve the overall efficiency of HVAC systems.
Building Information Modeling (BIM)
The integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM) with HVAC software is also gaining traction. BIM provides a comprehensive digital representation of a building, enabling engineers to design, analyze, and optimize HVAC systems within the context of the entire building. This approach enhances collaboration among architects, engineers, and contractors, leading to improved project outcomes.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies are emerging as valuable tools for HVAC design and modeling. VR allows engineers to experience a virtual representation of the building, while AR superimposes digital information onto the real-world environment. These technologies facilitate better visualization, collaboration, and decision-making during the design process.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
As the focus on sustainability and energy efficiency intensifies, HVAC software is evolving to meet these demands. Software developers are incorporating features that enable engineers to design systems that comply with green building standards, reduce energy consumption, and minimize environmental impact.
Conclusion
As we navigate the ever-evolving landscape of energy efficiency, HVAC software for energy modeling will continue to play a pivotal role. With ongoing advancements in technology and the increasing demand for sustainable solutions, this software will empower us to push the boundaries of energy optimization and create a more sustainable built environment.
Helpful Answers
What are the key benefits of using HVAC software for energy modeling?
HVAC software for energy modeling offers numerous benefits, including reduced energy consumption, lower operating costs, improved occupant comfort, enhanced design accuracy, and compliance with energy codes and regulations.
What are the different types of HVAC software available?
HVAC software for energy modeling can be categorized into three main types: simulation-based, rule-based, and data-driven. Each type has its own strengths and limitations, and the choice of software depends on the specific needs of the project.
What are the essential features to look for in HVAC software for energy modeling?
When selecting HVAC software for energy modeling, it is important to consider features such as user-friendliness, accuracy, flexibility, integration capabilities, and technical support.
How is HVAC software used in energy modeling applications?
HVAC software is used in a wide range of energy modeling applications, including building design optimization, energy audits, LEED certification, and utility rebate programs.
What are the emerging trends in HVAC software for energy modeling?
Emerging trends in HVAC software for energy modeling include the integration of artificial intelligence, cloud-based platforms, and real-time data analytics. These advancements are expected to enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility of energy modeling.