HVAC software for building simulation has revolutionized the design and operation of HVAC systems. With the ability to model and simulate the thermal and airflow performance of buildings, this software provides invaluable insights that can lead to improved energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and indoor air quality.
From energy modeling to system design and simulation, HVAC software offers a wide range of capabilities that cater to the specific needs of building professionals. This comprehensive guide will explore the different types of HVAC software available, discuss their benefits and challenges, and provide case studies and future trends that shape the industry.
Introduction
HVAC software for building simulation plays a vital role in the design, analysis, and optimization of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems in buildings. It provides a virtual environment where engineers and architects can simulate the performance of HVAC systems under various conditions, enabling them to make informed decisions about system design and operation.HVAC
software typically includes a comprehensive library of components, such as air handlers, chillers, boilers, and ducts, which can be used to create detailed models of HVAC systems. These models can then be used to simulate the system’s performance under different operating conditions, such as varying outdoor temperatures, occupancy levels, and equipment failures.
Types of HVAC Software
HVAC software is a powerful tool that can help engineers design and simulate HVAC systems. There are many different types of HVAC software available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The type of software that is right for you will depend on your specific needs.
Some of the most common types of HVAC software include:
Energy Modeling Software
Energy modeling software is used to predict the energy consumption of a building. This information can be used to design HVAC systems that are more efficient and cost-effective. Energy modeling software typically uses a variety of data, including weather data, building geometry, and occupancy patterns, to create a computer model of the building.
The model is then used to simulate the operation of the HVAC system and calculate the energy consumption.
Load Calculation Software
Load calculation software is used to calculate the heating and cooling loads of a building. This information is used to size the HVAC system and select the appropriate equipment. Load calculation software typically uses a variety of data, including weather data, building geometry, and occupancy patterns, to calculate the loads.
System Design Software
System design software is used to design the layout of the HVAC system. This software can be used to create a variety of different system configurations, including ductwork, piping, and equipment placement. System design software typically includes a library of HVAC components that can be used to create the design.
Simulation Software
Simulation software is used to simulate the operation of the HVAC system. This software can be used to predict the performance of the system and identify any potential problems. Simulation software typically uses a variety of data, including weather data, building geometry, and occupancy patterns, to create a computer model of the system.
The model is then used to simulate the operation of the system and calculate the performance.
Benefits of Using HVAC Software
HVAC software provides numerous advantages for building simulation, empowering engineers and designers to optimize HVAC system performance and enhance occupant well-being.
Key benefits include:
Improved Accuracy and Efficiency of HVAC System Design
HVAC software utilizes advanced algorithms and computational models to simulate the behavior of HVAC systems under varying conditions. This enables engineers to:
- Accurately predict system performance and energy consumption.
- Identify potential design flaws and optimize system configurations.
- Reduce the need for costly physical prototyping and testing.
Reduced Energy Consumption and Operating Costs
By optimizing HVAC system design, software helps reduce energy consumption and operating costs. Engineers can:
- Identify inefficiencies and implement energy-saving measures.
- Monitor system performance and make real-time adjustments.
- Meet energy efficiency standards and regulations.
Enhanced Occupant Comfort and Indoor Air Quality
HVAC software helps ensure occupant comfort and indoor air quality by:
- Simulating thermal conditions and predicting airflow patterns.
- Identifying potential sources of indoor air pollution.
- Optimizing ventilation systems to maintain healthy indoor air quality.
Challenges of Using HVAC Software
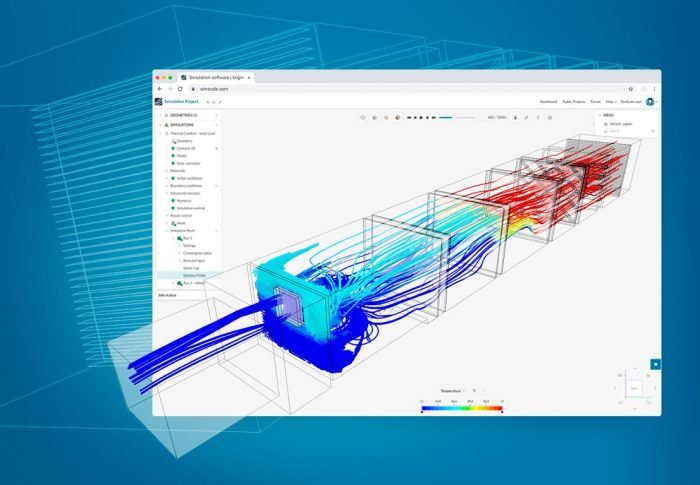
HVAC software, while powerful, is not without its challenges. These challenges can arise at various stages of the software’s usage, from data collection and input to model validation and calibration, and finally, the interpretation of results.
Understanding these challenges is crucial for effective software utilization and accurate simulation outcomes. HVAC professionals must be aware of these potential hurdles and take appropriate measures to mitigate their impact.
Data Collection and Input
Accurate HVAC simulations rely heavily on comprehensive and accurate data input. Gathering this data can be a time-consuming and complex process, especially for large and complex building models.
Some of the challenges associated with data collection and input include:
- Identifying and obtaining relevant data from various sources, such as building plans, equipment specifications, and operational schedules.
- Ensuring the consistency and compatibility of data from different sources.
- Managing large amounts of data, especially for complex building models.
- Dealing with missing or incomplete data, which can affect the accuracy of the simulation.
5. Case Studies
HVAC software has been widely used to improve the design and operation of HVAC systems in buildings. Here are some case studies and examples:
Reduced Energy Consumption in Commercial Buildings
A commercial building in New York City used HVAC software to optimize its HVAC system. The software identified areas where the system was inefficient and made recommendations for improvements. By implementing these recommendations, the building reduced its energy consumption by 15%.
Improved Indoor Air Quality in Healthcare Facilities
A hospital in California used HVAC software to design a new HVAC system for its critical care unit. The software helped the hospital to create a system that met the stringent indoor air quality requirements for healthcare facilities. The new system has significantly reduced the risk of infection for patients and staff.
Enhanced Comfort in Residential Buildings
A residential home in Florida used HVAC software to design a new HVAC system for its home. The software helped the homeowner to create a system that provides optimal comfort levels throughout the year. The new system has reduced the homeowner’s energy bills and improved their comfort.
6. Future Trends
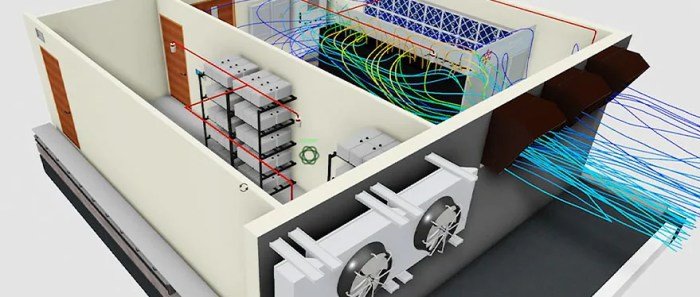
The future of HVAC software for building simulation is bright, with several emerging trends and advancements poised to shape the industry. These include the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), the rise of cloud-based software, and the integration of design tools.
AI and ML are already being used in HVAC software to automate tasks, improve accuracy, and optimize system performance. For example, AI can be used to identify patterns in energy consumption data and predict future energy usage. ML can be used to create virtual models of buildings that can be used to simulate different HVAC system configurations and identify the most efficient one.
Cloud-Based Software
Cloud-based HVAC software is becoming increasingly popular as it offers several advantages over traditional on-premises software. Cloud-based software is accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, which makes it ideal for remote teams and contractors. It is also typically more affordable than on-premises software, as there is no need to purchase and maintain hardware.
Integrated Design Tools
HVAC software is becoming increasingly integrated with other design tools, such as CAD and BIM software. This integration allows engineers to design and simulate HVAC systems within the context of the overall building design. This can help to identify potential conflicts early in the design process and ensure that the HVAC system is properly coordinated with the other building systems.
Final Thoughts
As the building industry continues to strive for sustainability and occupant well-being, HVAC software will play an increasingly critical role. By embracing emerging technologies and leveraging the power of simulation, building professionals can design and operate HVAC systems that meet the demands of the 21st century and beyond.
FAQ
What is the purpose of HVAC software for building simulation?
HVAC software for building simulation allows engineers and architects to model and simulate the thermal and airflow performance of buildings. This helps them design and operate HVAC systems that are more efficient, comfortable, and cost-effective.
What are the different types of HVAC software available?
There are various types of HVAC software available, including energy modeling software, load calculation software, system design software, and simulation software.
What are the benefits of using HVAC software for building simulation?
HVAC software for building simulation offers numerous benefits, including improved accuracy and efficiency of HVAC system design, reduced energy consumption and operating costs, and enhanced occupant comfort and indoor air quality.
What are the challenges of using HVAC software for building simulation?
Some challenges associated with using HVAC software include data collection and input, model validation and calibration, and interpretation of results.