In today’s competitive business landscape, customer relationship management (CRM) has emerged as a crucial aspect of driving growth and profitability. CRM analytics and reporting play a pivotal role in this ecosystem, providing invaluable insights that empower businesses to make informed decisions, optimize customer experiences, and maximize revenue.
By leveraging data from various sources, CRM analytics tools and techniques enable businesses to gain a comprehensive understanding of their customers’ behavior, preferences, and pain points. This data-driven approach empowers businesses to identify opportunities for improvement, personalize marketing campaigns, and enhance customer satisfaction.
CRM Analytics Fundamentals
CRM analytics is the practice of using data from a customer relationship management (CRM) system to improve customer relationships and drive business growth. CRM analytics can help businesses understand their customers’ needs and behaviors, identify opportunities for growth, and improve customer service.
There are many benefits to using CRM analytics, including:
- Improved customer understanding
- Increased sales and marketing effectiveness
- Improved customer service
- Reduced costs
There are many different types of CRM analytics, including:
- Customer segmentation
- Customer lifetime value
- Customer churn analysis
- Campaign performance analysis
The type of CRM analytics that is most appropriate for a particular business will depend on the business’s specific needs and goals.
Key CRM Metrics and KPIs
There are a number of key CRM metrics and KPIs that can be used to measure the effectiveness of CRM analytics. These metrics include:
- Customer acquisition cost
- Customer lifetime value
- Customer churn rate
- Sales conversion rate
- Marketing ROI
These metrics can be used to track the progress of CRM analytics initiatives and to identify areas for improvement.
Data Sources for CRM Analytics
CRM analytics relies on a variety of data sources to provide insights into customer behavior, preferences, and trends. These data sources can be internal or external, structured or unstructured, and can include:
* Internal data: This data is generated within the organization and includes customer relationship management (CRM) systems, sales data, marketing data, customer service data, and financial data.
* External data: This data is gathered from outside the organization and can include social media data, market research data, and data from third-party vendors.
Data quality is crucial for CRM analytics. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misleading insights and poor decision-making. It is important to ensure that data is accurate, complete, consistent, and timely. Data integration is also important to ensure that data from different sources can be combined and analyzed together.
Best practices for collecting and managing CRM data include:
* Establish clear data collection goals: Determine the specific business objectives that CRM analytics will support and identify the data needed to achieve those objectives.
* Use a variety of data sources: Collect data from multiple sources to get a comprehensive view of customer behavior.
* Clean and prepare data: Remove duplicate data, correct errors, and format data consistently.
* Integrate data from different sources: Combine data from different sources to create a single, unified view of the customer.
* Monitor data quality: Regularly review data quality to identify and address any issues.
CRM Analytics Tools and Techniques
CRM analytics tools empower businesses to extract valuable insights from their customer data. These tools offer a comprehensive range of features and capabilities, enabling organizations to analyze customer behavior, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
Various CRM analytics tools are available in the market, each with its unique strengths and weaknesses. Some popular tools include Salesforce Analytics Cloud, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Customer Insights, and Tableau CRM.
Comparison of CRM Analytics Tools
When selecting a CRM analytics tool, it is crucial to compare the features and capabilities of different options. Some key factors to consider include:
- Data sources supported
- Data visualization capabilities
- Reporting and dashboard functionality
- Predictive analytics capabilities
- Ease of use and accessibility
Using CRM Analytics Tools
CRM analytics tools can be used to analyze customer data in various ways. Some common use cases include:
- Identifying customer segments and trends
- Analyzing customer churn and retention rates
- Predicting customer behavior and preferences
- Optimizing marketing campaigns and customer engagement strategies
By leveraging CRM analytics tools, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their customers and make data-driven decisions to improve customer satisfaction, loyalty, and revenue.
Reporting and Visualization of CRM Analytics
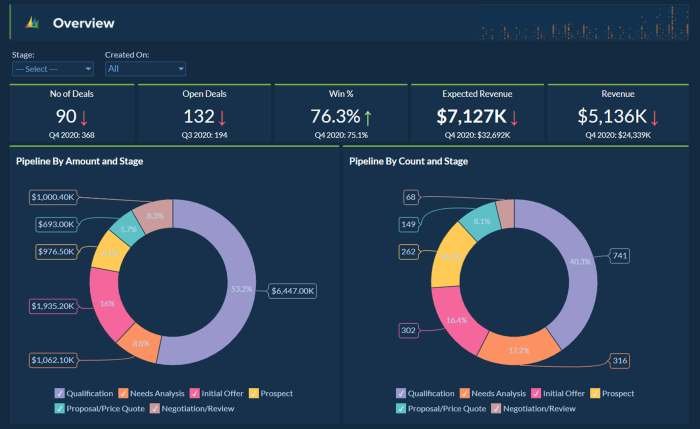
Reporting and visualization are crucial for effectively communicating CRM analytics results to stakeholders. They provide insights into customer behavior, sales performance, and other key metrics, enabling businesses to make informed decisions.
Creating effective CRM analytics reports and dashboards requires careful planning and design. Here are some guidelines to help you get started:
Designing Effective CRM Analytics Reports
- Define the purpose of the report: Determine the specific questions or insights the report aims to answer.
- Identify the target audience: Consider the level of technical expertise and business knowledge of the intended readers.
- Select relevant metrics: Choose metrics that align with the report’s purpose and provide valuable insights.
- Organize the report logically: Use clear headings, subheadings, and sections to guide readers through the report’s content.
- Use visuals sparingly: Charts and graphs can enhance the report’s readability, but avoid cluttering it with unnecessary visuals.
Creating Effective CRM Analytics Dashboards
- Determine the dashboard’s purpose: Define the specific business objectives the dashboard aims to support.
- Select relevant metrics: Choose metrics that provide a comprehensive view of the dashboard’s topic.
- Design a user-friendly interface: Use clear navigation, intuitive icons, and a visually appealing layout.
- Enable customization: Allow users to personalize the dashboard to suit their specific needs.
- Monitor and update the dashboard regularly: Ensure the dashboard remains relevant and up-to-date with the latest data.
Best Practices for Visualizing and Presenting CRM Analytics Results
- Use a variety of visualization techniques: Choose the most appropriate chart or graph type for each metric, considering factors such as data distribution and the desired insights.
- Label charts and graphs clearly: Use descriptive titles, axis labels, and legends to ensure readers can easily understand the data.
- Use color effectively: Color can highlight important trends and patterns, but avoid using too many colors or overly bright shades.
- Avoid unnecessary complexity: Keep visualizations simple and focused on conveying key insights.
- Test visualizations with users: Get feedback from stakeholders to ensure the visualizations are clear and effective.
Applications of CRM Analytics
CRM analytics plays a pivotal role in empowering businesses with actionable insights to drive informed decision-making and optimize customer relationships. Its applications extend across various business functions, enabling organizations to enhance customer satisfaction, increase sales, and streamline operations.
Let’s delve into specific use cases and case studies that demonstrate the tangible benefits of CRM analytics in different business functions:
Sales and Marketing
- Customer segmentation and targeting: CRM analytics helps businesses identify distinct customer segments based on demographics, behavior, and preferences. This enables targeted marketing campaigns and personalized messaging, leading to increased conversion rates.
- Lead scoring and qualification: CRM analytics tools can score and qualify leads based on their engagement and fit with the business. This allows sales teams to prioritize high-potential leads and allocate resources efficiently.
- Cross-selling and upselling opportunities: CRM analytics provides insights into customer purchase history, preferences, and cross-buying patterns. This information can be leveraged to identify opportunities for cross-selling and upselling complementary products or services.
Customer Service
- Customer churn prediction: CRM analytics models can identify customers at risk of churning. This enables proactive interventions, such as personalized offers or loyalty programs, to retain valuable customers.
- Case management and resolution: CRM analytics tools provide a comprehensive view of customer interactions, including case history, resolution time, and customer satisfaction ratings. This data can be used to identify areas for improvement in customer service processes.
- Customer feedback analysis: CRM analytics can analyze customer feedback from surveys, social media, and other channels. This feedback can be used to gauge customer sentiment, identify pain points, and improve product or service offerings.
Operations
- Resource optimization: CRM analytics can help businesses optimize resource allocation by analyzing customer demand patterns and identifying peak periods. This information can be used to schedule staff, allocate inventory, and ensure efficient operations.
- Inventory management: CRM analytics can provide insights into product demand, stock levels, and customer preferences. This information can be used to optimize inventory levels, reduce waste, and improve customer satisfaction.
- Fraud detection: CRM analytics can be used to detect fraudulent activities, such as suspicious orders or unauthorized access to customer data. This helps businesses protect their revenue and reputation.
Emerging Trends and Future Applications
CRM analytics is continuously evolving, with emerging trends and innovative applications shaping its future:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms are increasingly used in CRM analytics to automate data analysis, predict customer behavior, and provide personalized recommendations.
- Predictive Analytics: CRM analytics is moving towards predictive capabilities, enabling businesses to forecast future customer behavior and make proactive decisions.
- Customer Journey Mapping: CRM analytics can be used to map the customer journey across multiple touchpoints, providing insights into customer experience and opportunities for improvement.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, CRM analytics and reporting have become indispensable tools for businesses seeking to elevate their customer engagement strategies and achieve long-term success. By embracing the power of data analysis and leveraging the insights it provides, businesses can make smarter decisions, drive operational efficiency, and build lasting customer relationships.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the key benefits of CRM analytics?
CRM analytics provide businesses with actionable insights into customer behavior, enabling them to identify trends, optimize marketing campaigns, improve customer service, and drive revenue growth.
What are some common data sources used for CRM analytics?
CRM systems, social media platforms, customer surveys, website analytics, and email campaigns are common data sources for CRM analytics.
What are some best practices for visualizing CRM analytics results?
When visualizing CRM analytics results, it is important to use clear and concise charts and graphs, highlight key insights, and provide context to help decision-makers understand the implications of the data.