In the ever-evolving landscape of building management, optimizing HVAC systems is crucial for enhancing comfort, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. HVAC software with real-time data analytics has emerged as a game-changer, empowering facility managers with unprecedented insights into their HVAC systems’ performance.
This advanced software collects and analyzes data in real-time, enabling proactive decision-making and maximizing system efficiency. By harnessing the power of data analytics, HVAC systems can be fine-tuned to operate at optimal levels, leading to significant cost savings and improved occupant comfort.
Key Features of HVAC Software with Real-Time Data Analytics
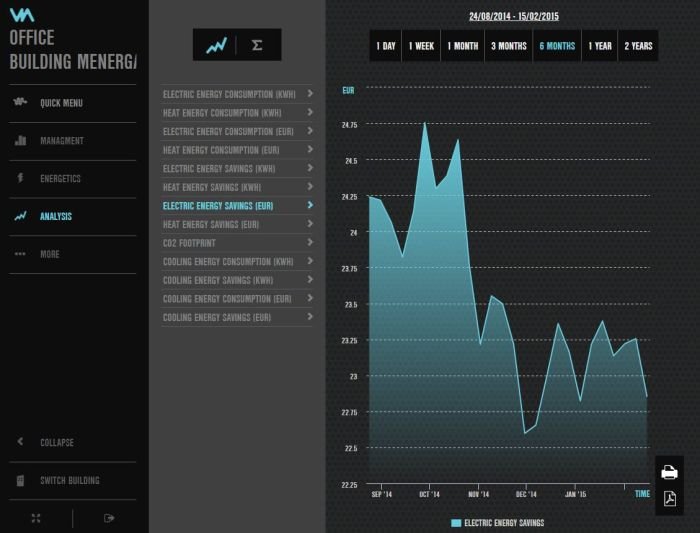
Real-time data analytics plays a crucial role in optimizing HVAC system performance and efficiency. HVAC software equipped with this capability offers numerous advantages, including:
- Enhanced monitoring and control
- Predictive maintenance
- Energy consumption optimization
- Improved occupant comfort
To facilitate real-time data analysis, HVAC software incorporates key features such as:
- Data collection and aggregation from sensors and IoT devices
- Real-time data visualization and dashboards
- Machine learning algorithms for anomaly detection and predictive analytics
- Integration with building management systems
These features enable HVAC systems to continuously monitor and analyze data, providing insights that can be leveraged to improve system performance and efficiency.
Data Collection and Aggregation
HVAC software with real-time data analytics collects data from various sources, including sensors, IoT devices, and building management systems. This data includes temperature, humidity, air quality, energy consumption, and equipment status. The software aggregates this data, providing a comprehensive view of the HVAC system’s operation.
Real-Time Data Visualization and Dashboards
Real-time data visualization and dashboards allow users to monitor and analyze data in real-time. Dashboards provide customizable visualizations that display key metrics, trends, and alerts. This enables users to quickly identify any issues or areas for improvement.
Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms are used to analyze data and identify patterns and anomalies. These algorithms can predict equipment failures, optimize energy consumption, and improve occupant comfort. For example, machine learning algorithms can analyze historical data to identify patterns in energy usage and suggest adjustments to reduce consumption.
Integration with Building Management Systems
Integration with building management systems (BMS) allows HVAC software to access data from other systems in the building, such as lighting, security, and fire detection. This integration provides a holistic view of the building’s operation, enabling HVAC systems to be optimized in conjunction with other systems.By
leveraging these key features, HVAC software with real-time data analytics empowers users to make data-driven decisions that enhance HVAC system performance and efficiency, ultimately leading to cost savings, improved occupant comfort, and a more sustainable building environment.
Types of Data Collected and Analyzed
HVAC software collects various types of data from sensors installed throughout the HVAC system. This data provides valuable insights into the system’s performance, enabling optimization and proactive maintenance.The collected data includes:
Temperature data
Monitors temperature levels at different points in the system, including supply and return air temperatures, indoor and outdoor temperatures, and equipment surface temperatures.
Humidity data
Measures humidity levels in the air, indicating moisture content and potential condensation issues.
Airflow data
Tracks airflow rates and patterns, ensuring proper ventilation and distribution of conditioned air throughout the building.
Pressure data
Monitors pressure levels in ducts, fans, and other system components, helping identify blockages, leaks, and pressure imbalances.
Energy consumption data
Collects data on energy usage by various system components, such as chillers, boilers, and fans, enabling energy efficiency analysis and optimization.
Real-Time Data Analysis for HVAC Optimization
Real-time data analysis plays a crucial role in optimizing HVAC system operations. By continuously monitoring and analyzing data, the software can:
Identify inefficiencies
Detect deviations from optimal operating parameters, such as excessive energy consumption, high humidity levels, or airflow imbalances.
Predict potential issues
Analyze trends and patterns in data to identify potential problems before they escalate, allowing for timely maintenance or adjustments.
Optimize system settings
Automatically adjust system settings, such as thermostat setpoints, fan speeds, and damper positions, to maintain optimal conditions and maximize energy efficiency.
Examples of Real-Time Data Analysis in Action
Identifying Airflow Imbalances
Data analysis can detect airflow imbalances by comparing airflow rates at different points in the system. This helps identify blocked or leaky ducts, allowing for prompt repair.
Predicting Equipment Failures
By monitoring equipment vibration, temperature, and energy consumption patterns, data analysis can predict potential equipment failures. This enables proactive maintenance, reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
Optimizing Energy Consumption
Real-time data analysis can identify periods of high energy consumption and suggest adjustments to system settings. For example, the software may recommend lowering thermostat setpoints during unoccupied hours or adjusting fan speeds to reduce energy usage.
Data Visualization and Reporting
HVAC software with real-time data analytics offers advanced visualization techniques to present complex data in an easily understandable format. Interactive dashboards and reports empower users to analyze data efficiently and make informed decisions.
Data Visualization Methods
Data visualization methods include:
- Time-series charts: Track data over time, enabling trend analysis and anomaly detection.
- Scatter plots: Display relationships between variables, highlighting correlations and outliers.
- Histograms: Show data distribution, providing insights into the frequency and range of values.
- Heat maps: Visualize data as a grid of colored cells, highlighting patterns and relationships.
Interactive Dashboards and Reports
Interactive dashboards provide real-time data visualization, allowing users to:
- Drill down into data: Explore details and context behind specific data points.
- Customize views: Tailor dashboards to specific needs and preferences.
- Create custom alerts: Set notifications for critical events or threshold violations.
Customizable Reporting
Customizable reporting enables users to generate reports tailored to their specific needs. This is important because:
- Stakeholder-specific reports: Different stakeholders, such as facility managers and engineers, require different types of information.
- Flexible report formats: Reports can be exported in various formats, such as PDF, Excel, or CSV, for easy sharing and analysis.
- Scheduled reporting: Automated report delivery ensures timely access to critical information.
Integration with Other Building Systems
Integrating HVAC software with other building systems offers significant benefits by enabling seamless data exchange and coordinated control. This enhances overall building performance, optimizes energy consumption, and improves occupant comfort.
For instance, integrating with lighting systems allows for demand-based lighting, adjusting illumination levels based on occupancy and daylight availability. This reduces energy waste and improves occupant satisfaction.
Security System Integration
Integrating with security systems enhances building safety and security. HVAC systems can be programmed to automatically adjust ventilation rates based on security events, such as smoke detection or unauthorized access. This ensures proper air quality and prevents the spread of contaminants.
Energy Management System Integration
Integrating with energy management systems provides real-time energy consumption data. This enables comprehensive energy analysis, identifying areas for optimization and reducing operational costs. By leveraging advanced algorithms, HVAC systems can be optimized to operate efficiently, reducing energy consumption without compromising comfort.
However, system integration also presents challenges. Data compatibility, communication protocols, and cybersecurity measures need to be carefully considered to ensure seamless integration and prevent system vulnerabilities.
Security and Data Privacy
HVAC software incorporates robust security measures to safeguard sensitive data. These measures include encryption, access control, and regular security audits to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber threats.
Data Privacy and Compliance
HVAC data privacy is crucial as it often includes sensitive information related to building occupants and energy consumption. The software complies with industry regulations, such as HIPAA and GDPR, to ensure data privacy and confidentiality.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
HVAC software with real-time data analytics offers substantial cost savings and efficiency gains. By monitoring and analyzing key HVAC parameters, organizations can optimize system performance, reduce energy consumption, and proactively address maintenance issues.
Return on Investment (ROI) Considerations
Evaluating the ROI of HVAC software involves considering several factors, including:
- Energy savings: Real-time data analytics enables precise control of HVAC systems, leading to reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills.
- Maintenance cost reduction: Predictive analytics can identify potential equipment failures, allowing for timely maintenance and preventing costly breakdowns.
- Improved occupant comfort: Data analytics helps ensure optimal temperature and humidity levels, enhancing occupant comfort and productivity.
- Increased equipment lifespan: Proactive maintenance based on data insights extends the lifespan of HVAC equipment, reducing replacement costs.
Final Summary
HVAC software with real-time data analytics has revolutionized the way we manage HVAC systems. Its ability to collect, analyze, and visualize data in real-time empowers facility managers with the insights they need to optimize performance, reduce costs, and enhance occupant comfort.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative and powerful features that will further transform the HVAC industry.
Q&A
What are the benefits of using HVAC software with real-time data analytics?
HVAC software with real-time data analytics provides numerous benefits, including improved system efficiency, reduced energy consumption, enhanced occupant comfort, and proactive maintenance.
How does real-time data analysis help optimize HVAC system performance?
Real-time data analysis allows facility managers to identify inefficiencies, diagnose problems, and make adjustments to system settings to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
What types of data are collected by HVAC software?
HVAC software collects various data points, including temperature, humidity, airflow, energy consumption, and equipment status, providing a comprehensive view of system performance.
How does HVAC software integrate with other building systems?
HVAC software can integrate with other building systems, such as lighting, security, and energy management systems, enabling centralized control and optimization of overall building performance.
What security measures are in place to protect data collected by HVAC software?
HVAC software typically employs robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular security updates, to ensure the privacy and integrity of collected data.