In the pursuit of sustainable building practices, HVAC software has emerged as an indispensable tool for optimizing energy consumption. By harnessing the power of data analysis and advanced algorithms, HVAC software empowers facility managers and building owners to gain unprecedented insights into their HVAC systems, enabling them to make informed decisions that reduce energy usage and enhance building performance.
As the world grapples with the urgency of climate change, HVAC software offers a practical and cost-effective solution to minimize our environmental impact while ensuring occupant comfort and productivity. Its ability to monitor, analyze, and control HVAC systems in real-time has made it a cornerstone of modern building management strategies.
Overview of HVAC Software for Energy Efficiency
HVAC software plays a crucial role in reducing energy consumption by optimizing the performance of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. It provides comprehensive tools and analytics that enable facility managers and engineers to monitor, control, and analyze energy usage, identify inefficiencies, and implement strategies to improve system performance.
By leveraging advanced algorithms and data analysis techniques, HVAC software can optimize equipment operation, reduce energy waste, and improve overall energy efficiency. This leads to significant cost savings, reduced carbon emissions, and enhanced occupant comfort.
Examples of HVAC Software Solutions for Energy Reduction
Several HVAC software solutions focus specifically on energy reduction. These solutions provide features such as:
- Real-time monitoring of energy consumption
- Identification of energy-saving opportunities
- Generation of energy reports and analysis
li>Automated control of HVAC equipment
Examples of such software include:
- Siemens Building Technologies Navigator
- Honeywell Forge Energy Optimization
- Johnson Controls Metasys
Features and Capabilities of HVAC Software for Energy Consumption Reduction
HVAC software plays a crucial role in optimizing HVAC system performance and reducing energy consumption. It provides a comprehensive suite of features and capabilities that enable facility managers and HVAC technicians to monitor, analyze, and control HVAC systems in real-time, resulting in significant energy savings.The
key features and capabilities of HVAC software include:
- Real-time monitoring and data collection: HVAC software continuously monitors and collects data from various sensors installed throughout the HVAC system. This data includes temperature, humidity, airflow, and energy consumption. By collecting and analyzing this data, the software provides valuable insights into the system’s performance and identifies areas for improvement.
- System optimization: HVAC software uses advanced algorithms to optimize the performance of HVAC systems. It can automatically adjust setpoints, control fan speeds, and optimize airflow patterns to ensure the system operates at peak efficiency. By optimizing the system’s performance, the software can reduce energy consumption and improve comfort levels.
- Predictive maintenance: HVAC software can predict potential equipment failures and maintenance needs based on historical data and real-time monitoring. This allows facility managers to schedule maintenance proactively, preventing costly breakdowns and unplanned downtime. Predictive maintenance also helps extend the lifespan of HVAC equipment and reduces repair costs.
- Fault detection and diagnostics: HVAC software can detect and diagnose faults in the HVAC system. It continuously monitors system parameters and compares them to predefined thresholds. If any parameter exceeds the threshold, the software generates an alert, allowing facility managers to quickly identify and resolve the issue. Fault detection and diagnostics help prevent minor issues from escalating into major problems, reducing downtime and energy waste.
- Energy reporting and analysis: HVAC software provides comprehensive energy reporting and analysis capabilities. It can track energy consumption over time, identify trends, and compare performance to industry benchmarks. This information helps facility managers understand the energy consumption patterns of their HVAC system and make informed decisions to reduce energy usage.
Implementation and Integration of HVAC Software for Energy Savings
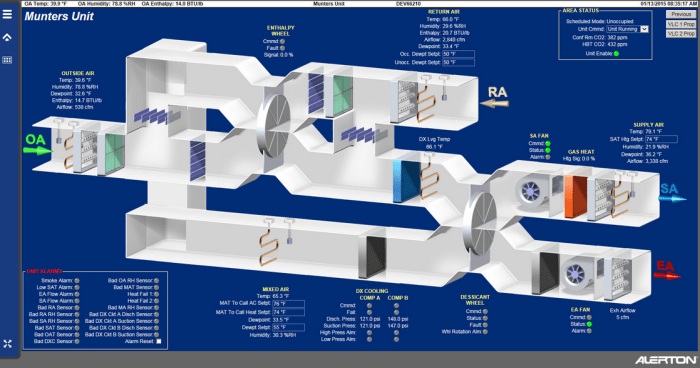
Implementing and integrating HVAC software for energy efficiency involves a systematic process that encompasses several key steps:
Software Installation and Configuration
The initial step involves installing the HVAC software on the designated computer or server. This may require specific system requirements and configurations to ensure compatibility and optimal performance. Once installed, the software needs to be configured based on the specific HVAC system and building characteristics.
This includes defining system parameters, equipment schedules, and control strategies to optimize energy consumption.
Integration with Building Management Systems
For seamless operation and data exchange, HVAC software should be integrated with existing building management systems (BMS). This integration enables centralized control and monitoring of HVAC systems alongside other building functions such as lighting, security, and access control. By leveraging BMS capabilities, HVAC software can optimize energy consumption based on real-time building conditions and occupant behavior.
Data Analysis and Reporting for Energy Efficiency Optimization
HVAC software provides robust data analysis capabilities to monitor energy efficiency and optimize performance. It collects real-time data from sensors and building automation systems, including temperature, humidity, and energy consumption. Advanced analytics tools within the software analyze this data to identify patterns, trends, and inefficiencies in energy usage.
Report Generation and Insights
HVAC software generates comprehensive reports that provide insights into energy consumption patterns. These reports typically include:
- Historical data and trend analysis of energy usage
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) for energy efficiency, such as energy intensity and carbon footprint
- Comparison of energy consumption against industry benchmarks
- Identification of areas with high energy consumption and potential for optimization
Identifying Areas for Optimization
Data analysis helps identify specific areas where energy optimization can be achieved. For example, the software may reveal that a particular zone in the building is consistently consuming more energy than others. This insight can lead to targeted energy-saving measures, such as adjusting temperature setpoints, optimizing equipment schedules, or implementing demand-response strategies.
Case Studies and Examples of HVAC Software Implementation for Energy Savings
HVAC software has been successfully implemented in various organizations, leading to significant energy savings and improved building performance. Here are some case studies and examples that demonstrate the benefits of HVAC software for energy efficiency:
Energy Savings at a University Campus
A large university campus implemented HVAC software to optimize the operation of its heating and cooling systems. The software used real-time data to adjust temperature setpoints, fan speeds, and equipment schedules based on occupancy and weather conditions. As a result, the campus reduced its energy consumption by 15% and saved over $1 million in annual energy costs.
Improved Building Performance at a Commercial Office Building
A commercial office building installed HVAC software to improve the comfort and productivity of its occupants. The software monitored indoor air quality, temperature, and humidity levels, and automatically adjusted HVAC system settings to maintain optimal conditions. The building achieved a LEED Gold certification and increased occupant satisfaction by 20%.
Reduced Carbon Emissions at a Manufacturing Facility
A manufacturing facility implemented HVAC software to reduce its carbon emissions. The software analyzed energy consumption data and identified opportunities for improvement. The facility made operational changes and installed energy-efficient equipment, resulting in a 10% reduction in carbon emissions and a 5% increase in production output.
Closure
In conclusion, HVAC software has proven to be a game-changer in the realm of energy efficiency. Its ability to optimize HVAC system performance, provide data-driven insights, and facilitate seamless integration with existing building management systems makes it an invaluable asset for any organization seeking to reduce its energy footprint and create a more sustainable future.
As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect even greater advancements in energy efficiency, further driving down operating costs and minimizing our impact on the environment.
FAQ
What are the key benefits of using HVAC software for energy efficiency?
HVAC software offers numerous benefits for energy efficiency, including real-time monitoring of system performance, automated optimization of HVAC settings, and detailed reporting on energy consumption patterns. This data-driven approach empowers users to identify areas for improvement, reduce energy waste, and optimize system efficiency.
How does HVAC software integrate with existing building management systems?
HVAC software is designed to seamlessly integrate with most building management systems (BMS), allowing for centralized control and monitoring of all building systems. This integration enables HVAC software to access real-time data from sensors, controllers, and other devices, providing a comprehensive view of building performance and energy consumption.
What are some real-world examples of HVAC software implementations for energy savings?
Numerous organizations have successfully implemented HVAC software to achieve significant energy savings. For instance, a large university reduced its energy consumption by 15% after implementing an HVAC software solution that optimized system settings and provided real-time monitoring. Another example is a commercial office building that achieved a 20% reduction in energy costs by using HVAC software to identify and address inefficiencies in its HVAC system.