In the modern world of building management, efficiency and comfort are paramount. HVAC systems play a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable indoor environment, but their effectiveness can be greatly enhanced through integration with other systems.
HVAC software that integrates with other systems offers a range of benefits, from improved energy efficiency to enhanced occupant comfort. This integration allows for seamless communication between HVAC systems and other building systems, such as lighting, security, and fire safety, creating a truly intelligent and responsive building environment.
Overview of HVAC Software Integration
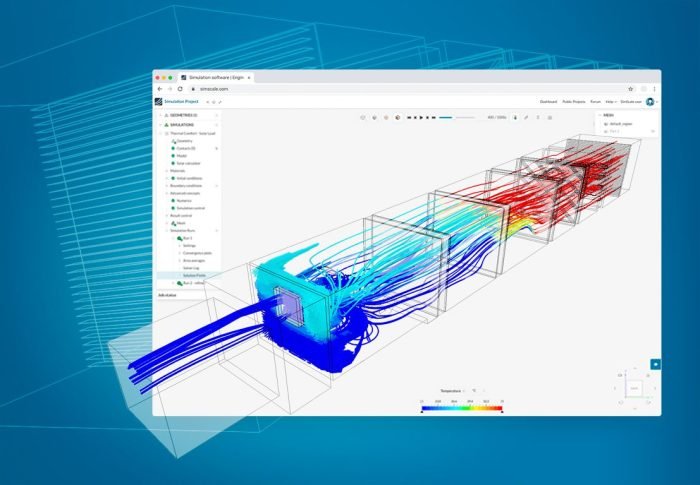
The integration of HVAC software with other systems involves connecting the HVAC system to other software applications or platforms to enhance its functionality and streamline operations. This integration allows HVAC systems to exchange data and communicate with other systems, leading to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced comfort.
HVAC software integration offers numerous benefits, including:
- Centralized control and monitoring of all HVAC systems from a single platform
- Automated scheduling and optimization of HVAC operations
- Remote access and control of HVAC systems
- Enhanced energy efficiency and reduced operating costs
- Improved occupant comfort and satisfaction
However, HVAC software integration also presents certain challenges:
- Compatibility issues between different software systems
- Data security and privacy concerns
- Cost and complexity of implementation
Despite these challenges, HVAC software integration has proven successful in various applications:
- Integration with building automation systems (BAS) for centralized control of all building systems
- Integration with energy management systems (EMS) for optimized energy consumption
- Integration with occupant engagement platforms for personalized comfort control
Types of HVAC Software Integration
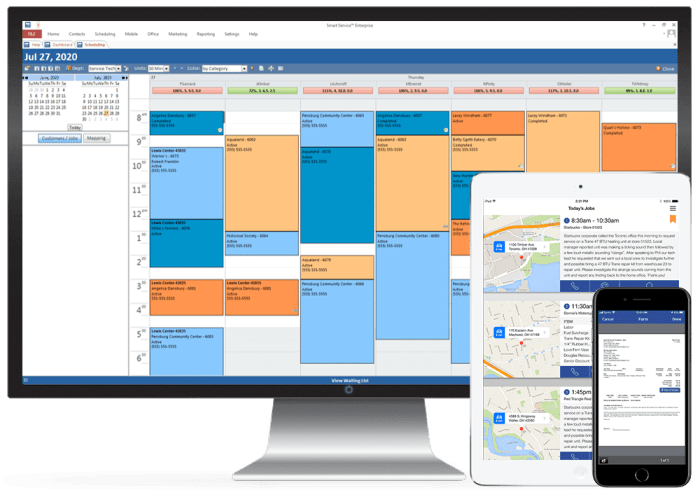
HVAC software integration involves connecting different software systems to enhance the functionality and efficiency of HVAC systems. There are several types of HVAC software integration, each with its unique features, capabilities, advantages, and disadvantages.
The most common types of HVAC software integration include:
Building Automation Systems (BAS) Integration
BAS integration allows HVAC software to connect with other building systems, such as lighting, security, and fire alarm systems. This integration enables centralized control and monitoring of all building systems, optimizing energy consumption, improving occupant comfort, and enhancing overall building efficiency.
Energy Management Systems (EMS) Integration
EMS integration connects HVAC software with energy management systems to monitor and control energy consumption. This integration provides real-time data on energy usage, allowing facility managers to identify areas for improvement and implement energy-saving measures.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Integration
CAD integration enables HVAC software to interact with CAD drawings. This integration allows designers to create and modify HVAC designs within the CAD software and seamlessly transfer them to the HVAC software for further analysis and optimization.
Building Information Modeling (BIM) Integration
BIM integration connects HVAC software with BIM models. This integration allows HVAC designers to access and utilize building information from the BIM model, such as architectural plans, structural details, and MEP systems. This integration enhances design accuracy, reduces errors, and improves collaboration among project stakeholders.
Benefits of HVAC Software Integration
Integrating HVAC software with other systems offers a range of advantages that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve occupant comfort.
By connecting HVAC systems to building management systems (BMS), facility managers gain centralized control over multiple building systems. This integration enables remote monitoring and adjustment of HVAC settings, reducing the need for manual interventions and improving operational efficiency.
Enhanced Efficiency
- Centralized control allows for optimized scheduling, ensuring HVAC systems operate only when necessary.
- Integration with sensors and analytics enables real-time monitoring of energy consumption, identifying areas for improvement.
- Automated fault detection and diagnostics reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
Reduced Costs
- Optimized scheduling minimizes energy consumption, leading to significant savings on utility bills.
- Predictive maintenance based on real-time data reduces unplanned downtime and extends equipment life.
- Remote monitoring and control eliminate the need for on-site visits, saving labor costs.
Improved Comfort
- Integration with sensors ensures optimal temperature and humidity levels, enhancing occupant comfort.
- Demand-controlled ventilation systems adjust ventilation rates based on occupancy, improving air quality.
- Remote access allows occupants to adjust settings from anywhere, providing personalized comfort.
Case Study: A university integrated its HVAC system with a BMS. The integration resulted in a 20% reduction in energy consumption, a 15% decrease in maintenance costs, and improved occupant satisfaction due to better temperature control.
Challenges of HVAC Software Integration
Integrating HVAC software with other systems can present various challenges. These include:
- Compatibility issues: Ensuring compatibility between different software systems can be complex, especially if they are from different vendors or use different protocols.
- Data security concerns: Integrating HVAC software with other systems can raise data security concerns, as it may involve sharing sensitive information such as building blueprints, energy consumption data, and occupant information.
- User adoption challenges: End-users may face challenges in adopting new HVAC software, especially if it requires significant training or changes to existing workflows.
Overcoming Challenges
To overcome these challenges, it is important to:
- Conduct thorough compatibility testing before integrating HVAC software with other systems.
- Implement robust data security measures, such as encryption and access controls, to protect sensitive information.
- Provide comprehensive training and support to end-users to ensure smooth adoption of the new software.
Best Practices for HVAC Software Integration
Successful HVAC software integration requires careful planning, implementation, and maintenance. Here are some best practices to consider:
Planning
- Define clear goals and objectives for the integration.
- Identify all stakeholders and their roles in the process.
- Choose software that is compatible with existing systems and meets the specific needs of the organization.
Implementation
- Establish a dedicated project team with the necessary expertise.
- Develop a detailed implementation plan that includes timelines, resources, and communication protocols.
- Test the integrated system thoroughly before going live.
Maintenance
- Monitor the integrated system regularly for performance and security issues.
- Apply software updates and patches as needed.
- Train staff on the use and maintenance of the integrated system.
Checklist for HVAC Software Integration
Consider the following checklist when implementing HVAC software integration:
- Define integration goals and objectives.
- Identify stakeholders and their roles.
- Select compatible software.
- Establish a project team.
- Develop an implementation plan.
- Test the integrated system.
- Establish monitoring protocols.
- Plan for software updates.
- Train staff on the integrated system.
By following these best practices, organizations can ensure successful HVAC software integration that optimizes building performance, reduces energy consumption, and improves occupant comfort.
Future Trends in HVAC Software Integration
HVAC software integration is poised to undergo significant advancements driven by emerging technologies. These trends will shape the future of HVAC systems and enhance their efficiency, reliability, and sustainability.
Role of IoT, Cloud Computing, and AI in Future Integrations
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices will connect HVAC systems to a network, enabling remote monitoring, control, and data collection. This will facilitate predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and enhanced occupant comfort. Cloud Computing: Cloud-based platforms will provide a centralized repository for HVAC data, allowing for remote access, analysis, and insights.
This will enable real-time monitoring, data-driven decision-making, and improved system performance. Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms will analyze HVAC data to identify patterns, predict system behavior, and optimize operations. This will lead to automated fault detection, self-tuning systems, and personalized comfort settings.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities for Future Developments
Data Security: As HVAC systems become more connected, ensuring data security and privacy will be critical. Robust cybersecurity measures will be necessary to protect sensitive information. Interoperability: Integrating different HVAC systems and software solutions can be challenging.
Open standards and interoperability protocols will be essential to facilitate seamless data exchange. Skilled Workforce: The adoption of advanced technologies will require a skilled workforce with expertise in IoT, cloud computing, and AI. Training and development programs will be necessary to bridge the skills gap.
Opportunities for Innovation: The integration of emerging technologies opens up new opportunities for innovation. HVAC manufacturers and software developers can collaborate to create integrated solutions that meet the evolving needs of the industry.
Outcome Summary
Integrating HVAC software with other systems is a transformative step towards optimizing building performance. By leveraging the power of integration, building managers can achieve significant energy savings, enhance occupant comfort, and create a more sustainable and efficient built environment.
Questions and Answers
What are the key benefits of integrating HVAC software with other systems?
Integrating HVAC software with other systems offers numerous benefits, including improved energy efficiency, reduced operating costs, enhanced occupant comfort, and increased system reliability.
What are the common challenges associated with integrating HVAC software with other systems?
Some common challenges include compatibility issues between different systems, data security concerns, and the need for user training. However, these challenges can be overcome with proper planning and implementation.
What are the best practices for successful HVAC software integration?
Best practices include thorough planning, careful selection of software and hardware, proper installation and configuration, and ongoing maintenance and support.
What are the emerging trends in HVAC software integration?
Emerging trends include the use of IoT (Internet of Things) devices, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence (AI) to further enhance the integration and optimization of HVAC systems.