In today’s dynamic and energy-conscious world, HVAC systems play a crucial role in ensuring comfort, productivity, and energy efficiency in our buildings. HVAC software with real-time data monitoring has emerged as a game-changer in the industry, providing invaluable insights and empowering facility managers with unprecedented control over their HVAC operations.
This advanced software seamlessly integrates with HVAC systems, enabling real-time monitoring of critical parameters, remote control, and comprehensive data analysis. By harnessing the power of data, HVAC software empowers users to optimize energy consumption, minimize downtime, and proactively address maintenance issues, ultimately leading to enhanced building performance and reduced operating costs.
Real-Time Data Monitoring
Real-time data monitoring in HVAC systems provides valuable insights into system performance, energy consumption, and occupant comfort. It enables facility managers to make informed decisions, optimize system operation, and reduce energy costs.Remote monitoring and control allow facility managers to access and control HVAC systems from anywhere, at any time.
This enables them to respond quickly to system issues, adjust settings remotely, and ensure optimal performance even when not on-site.Examples of real-time data that can be monitored include:
- Temperature and humidity levels
- Airflow rates
- Equipment status and alarms
- Energy consumption
- Occupancy levels
By monitoring these parameters in real-time, facility managers can identify trends, diagnose issues, and implement corrective actions to maintain optimal system performance and occupant comfort.
Data Analysis and Visualization
HVAC data analysis and visualization are essential for identifying trends, patterns, and opportunities for improvement. By analyzing data from sensors, meters, and other sources, facility managers can gain insights into system performance, energy consumption, and occupant comfort.
Types of Data Analysis
HVAC data analysis can involve various types of analysis, including:
- Descriptive analysis: Provides a summary of data, such as averages, minimums, maximums, and trends.
- Diagnostic analysis: Identifies the root causes of problems, such as equipment failures or operational inefficiencies.
- Predictive analysis: Uses historical data to predict future events, such as equipment failures or energy consumption.
- Prescriptive analysis: Recommends actions to improve system performance, such as adjusting setpoints or replacing equipment.
Data Visualization
Data visualization is a powerful tool for presenting data in a clear and concise way. It can help facility managers identify trends and patterns that would be difficult to spot from raw data alone.
Common types of data visualizations used in HVAC include:
- Charts: Line charts, bar charts, and pie charts can show data trends and comparisons.
- Graphs: Scatter plots and heat maps can show relationships between variables.
- Dashboards: Dashboards provide a consolidated view of key performance indicators (KPIs) and other data.
- Reports: Reports can provide detailed information about system performance, energy consumption, and occupant comfort.
Examples of Dashboards and Reports
Examples of dashboards and reports that can be generated from HVAC data include:
- Energy consumption dashboard: Shows energy consumption data by hour, day, week, or month.
- Equipment performance report: Provides detailed information about the performance of individual pieces of equipment.
- Occupant comfort report: Summarizes data on occupant comfort, such as temperature and humidity levels.
Fault Detection and Diagnostics
HVAC software plays a crucial role in detecting and diagnosing faults within HVAC systems. These faults can range from minor issues to critical failures, and early detection is essential to prevent costly downtime and maintain optimal system performance.HVAC software employs various fault detection algorithms to identify and diagnose faults.
These algorithms analyze real-time data from sensors and controllers to detect anomalies in system behavior. Common algorithms include rule-based systems, statistical models, and machine learning techniques.
Rule-Based Systems
Rule-based systems use a set of predefined rules to identify faults. These rules are based on expert knowledge and historical data. When the software detects a condition that matches a rule, it triggers an alert and provides a possible diagnosis.
Statistical Models
Statistical models use historical data to create a baseline for normal system operation. When the software detects deviations from this baseline, it can identify potential faults. Statistical models are particularly effective in detecting gradual changes in system performance.
Machine Learning Techniques
Machine learning techniques use algorithms that learn from historical data to identify patterns and anomalies. These algorithms can be trained to detect faults that are not easily identifiable using rule-based or statistical models. Machine learning techniques are becoming increasingly popular in HVAC fault detection due to their ability to handle complex and non-linear relationships in data.Fault
detection can significantly reduce downtime by enabling early intervention. By identifying faults before they escalate into major failures, HVAC software can help businesses avoid costly repairs, production losses, and customer dissatisfaction.
Energy Efficiency Optimization
HVAC software can play a crucial role in optimizing energy efficiency, leading to significant cost savings and environmental benefits. It provides real-time data monitoring and analytics that enable facility managers to identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to reduce energy consumption.One
key strategy for energy efficiency improvement is to optimize equipment performance. HVAC software can monitor equipment performance parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and airflow, and identify any deviations from optimal operating conditions. This allows for timely maintenance and adjustments to ensure that equipment is operating at peak efficiency.Another
strategy is to optimize system operation. HVAC software can analyze system performance data and identify opportunities for load shifting, demand response, and other operational adjustments that can reduce energy consumption. For example, the software can automatically adjust the setpoint temperatures or turn off equipment during periods of low occupancy or low demand.Energy
efficiency optimization can lead to substantial operating cost savings. Studies have shown that HVAC software can reduce energy consumption by up to 30%, resulting in significant savings on utility bills. Additionally, optimizing energy efficiency can extend the lifespan of HVAC equipment, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
Maintenance and Repair Management
HVAC software can help manage maintenance and repairs by providing a centralized platform to track all maintenance activities. This can help to improve system reliability and reduce downtime.The different types of maintenance tasks that can be tracked include:
- Preventive maintenance
- Corrective maintenance
- Emergency repairs
Preventive maintenance is performed on a regular basis to prevent problems from occurring. Corrective maintenance is performed to fix problems that have already occurred. Emergency repairs are performed to fix problems that pose an immediate threat to safety or property.Maintenance
management can improve system reliability by ensuring that all maintenance tasks are performed on time and to the correct standard. This can help to prevent problems from occurring in the first place and can also help to ensure that problems are fixed quickly and efficiently.
Integration with Other Systems
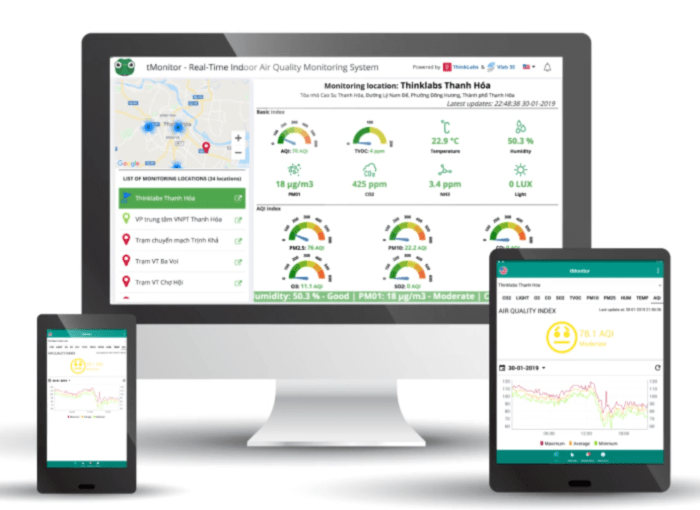
Integrating HVAC software with other building systems is crucial for optimizing building performance and occupant comfort. It allows for centralized control, data sharing, and automated responses, leading to improved efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and enhanced occupant satisfaction.
HVAC software can be integrated with various systems, including:
- Building Management Systems (BMS): Provides centralized control and monitoring of all building systems, including HVAC, lighting, security, and fire safety.
- Energy Management Systems (EMS): Monitors and controls energy consumption, enabling energy-saving strategies and reducing operating costs.
- Lighting Control Systems: Integrates with HVAC systems to optimize lighting levels based on occupancy and daylight availability, reducing energy consumption and improving occupant comfort.
- Security Systems: Allows HVAC systems to be controlled remotely in case of emergencies, such as fire or security breaches.
Integration with other systems enables:
- Centralized Monitoring and Control: Real-time monitoring of all building systems from a single platform, allowing for quick troubleshooting and adjustments.
- Automated Responses: Configuring automated responses to events, such as adjusting HVAC settings based on occupancy or energy demand, optimizing performance.
- Data Sharing and Analysis: Sharing data between systems provides insights into building performance, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Improved Energy Efficiency: Coordinating HVAC systems with other systems reduces energy waste and optimizes energy consumption.
Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based HVAC software solutions offer numerous benefits, including increased flexibility, scalability, and remote accessibility. These solutions are hosted on remote servers, allowing users to access their HVAC systems from any location with an internet connection.
Types of Cloud-Based Solutions
There are several types of cloud-based HVAC software solutions available, each designed to meet specific needs. These include:
- Monitoring and Control: These solutions provide real-time monitoring and control of HVAC systems, allowing users to remotely adjust settings, troubleshoot issues, and optimize performance.
- Energy Management: These solutions help users track and analyze energy consumption, identify inefficiencies, and implement energy-saving measures.
- Predictive Maintenance: These solutions use machine learning algorithms to predict potential equipment failures, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Integration: These solutions integrate with other building management systems, such as lighting, security, and access control, providing a comprehensive view of building operations.
Flexibility and Scalability
Cloud-based solutions offer unparalleled flexibility and scalability. They can be easily customized to meet the specific needs of any HVAC system, regardless of size or complexity. As the system grows or changes, the software can be scaled up or down to accommodate the new requirements.For
example, a small business with a single HVAC unit can use a basic monitoring and control solution. As the business grows and adds more units, the software can be scaled up to provide comprehensive energy management and predictive maintenance capabilities.
Summary
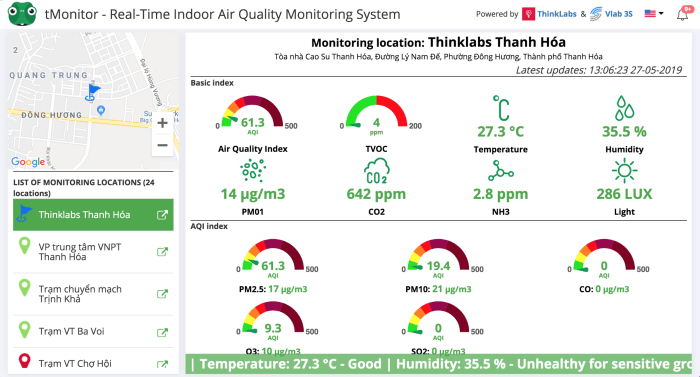
In conclusion, HVAC software with real-time data monitoring is an indispensable tool for modern facility management. It empowers users with actionable insights, enabling them to make informed decisions that optimize energy efficiency, improve system reliability, and enhance occupant comfort. As technology continues to advance, the integration of cloud-based solutions and advanced analytics will further revolutionize the HVAC industry, unlocking even greater potential for efficiency, sustainability, and cost savings.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the benefits of real-time data monitoring in HVAC systems?
Real-time data monitoring provides a comprehensive overview of system performance, enabling early detection of anomalies, proactive maintenance, and optimized energy consumption.
How does data visualization aid in identifying trends and patterns?
Data visualization presents complex data in graphical formats, making it easier to identify patterns, trends, and correlations that may not be apparent from raw data.
What are some examples of fault detection algorithms used in HVAC software?
Common fault detection algorithms include rule-based systems, statistical methods, and machine learning algorithms, each tailored to specific fault types and system characteristics.
How can HVAC software assist in maintenance and repair management?
HVAC software provides a centralized platform for tracking maintenance tasks, scheduling repairs, and managing spare parts inventory, ensuring efficient and timely maintenance.
What are the advantages of cloud-based HVAC software solutions?
Cloud-based solutions offer remote access, scalability, automatic updates, and enhanced data security, enabling facility managers to monitor and control their HVAC systems from anywhere.