Life insurance is a crucial financial tool that provides peace of mind and financial security for loved ones in the event of an untimely demise. At the heart of life insurance lies the death benefit, a sum of money paid to designated beneficiaries upon the policyholder’s passing. Understanding the intricacies of the death benefit is essential for maximizing its potential and ensuring that your legacy aligns with your wishes.
The death benefit serves as a financial cushion, providing funds to cover expenses such as funeral costs, outstanding debts, and future financial obligations. It can also be used to support loved ones, ensuring their financial stability and well-being.
Death Benefit Overview
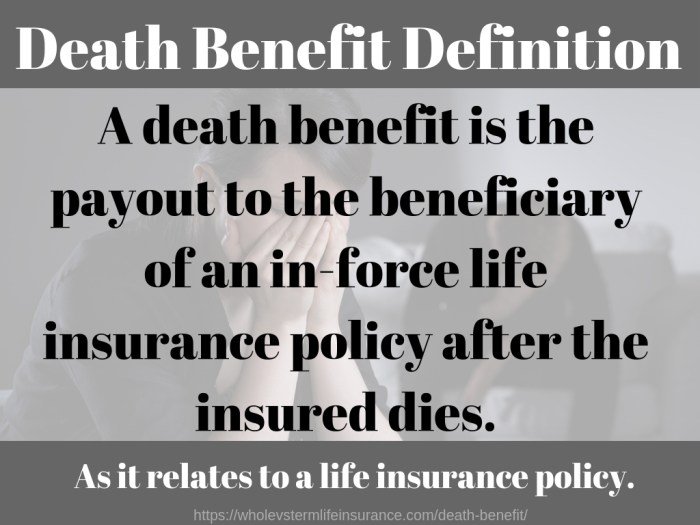
A death benefit is a payment made by a life insurance company to the beneficiaries of an insured person upon their death. It is the primary purpose of life insurance and provides financial protection to the policyholder’s loved ones in the event of their untimely demise.
The death benefit is typically calculated based on the face value of the policy, which is the amount of coverage purchased by the insured person. Additional factors that may affect the death benefit include the age, health, and lifestyle of the insured, as well as the type of life insurance policy they have.
Calculating the Death Benefit
The formula for calculating the death benefit is generally as follows:
Death Benefit = Face Value + Additional Benefits – Deductions
The face value is the primary amount of coverage, while additional benefits may include riders or supplemental coverage that provides extra protection, such as coverage for accidental death or dismemberment. Deductions may include outstanding loans or withdrawals against the policy.
Payment of the Death Benefit
Upon the death of the insured person, the beneficiaries named on the policy file a claim with the life insurance company. The company will review the claim and, if approved, will pay out the death benefit according to the terms of the policy.
The death benefit can be paid in a lump sum or as an annuity over a period of time. The beneficiaries can choose how the death benefit is paid out based on their financial needs and preferences.
Beneficiaries and Assignments
When purchasing a life insurance policy, it is crucial to designate beneficiaries who will receive the death benefit upon your passing. The process of naming beneficiaries involves specifying individuals or entities who will be legally entitled to the proceeds of the policy.
Assigning a death benefit to a specific person or entity involves transferring ownership of the policy or a portion of it. This can be done for various reasons, such as ensuring that the proceeds are distributed according to your wishes or providing financial support to a particular individual or organization.
Primary Beneficiary
The primary beneficiary is the individual or entity who receives the majority or entirety of the death benefit. They are typically designated at the time the policy is purchased and can be changed at any time by the policyholder.
Contingent Beneficiary
A contingent beneficiary is named to receive the death benefit if the primary beneficiary predeceases the policyholder or is otherwise unable to receive the proceeds. Multiple contingent beneficiaries can be named, and the policyholder can specify the order in which they will receive the benefit.
Revocable and Irrevocable Beneficiaries
Beneficiaries can be either revocable or irrevocable. Revocable beneficiaries can be changed at any time by the policyholder, while irrevocable beneficiaries cannot. Irrevocable beneficiaries are typically named in a trust or other legal document that ensures they receive the death benefit regardless of any changes made by the policyholder.
Tax Implications
Understanding the tax implications of life insurance death benefits is crucial for both the insured and the beneficiaries. The treatment of death benefits varies depending on the tax jurisdiction and the specific circumstances of the policy.
Generally, life insurance death benefits are not subject to income tax for the beneficiaries. This means that the full amount of the death benefit is received tax-free. However, there are certain exceptions to this rule, such as if the death benefit is received in installments or if it is used to purchase an annuity.
Estate Tax
In some jurisdictions, life insurance death benefits may be subject to estate tax. Estate tax is a tax on the value of an individual’s assets at the time of their death. If the death benefit is included in the insured’s estate, it may be subject to estate tax. However, there are certain strategies that can be used to minimize or avoid estate tax on life insurance death benefits.
Estate Planning Considerations
Life insurance death benefits can play a crucial role in estate planning by providing liquidity to cover estate taxes and expenses, distributing assets to beneficiaries, and minimizing the overall tax burden.
The death benefit can be structured in various ways to achieve these goals:
Minimizing Estate Taxes
- The death benefit can be used to pay estate taxes, reducing the taxable value of the estate and potentially lowering the overall tax liability.
- Life insurance policies can be structured as irrevocable trusts, which remove the proceeds from the insured’s estate, further reducing estate taxes.
Distributing Assets
- The death benefit can be used to distribute assets to beneficiaries in a manner that is not subject to probate, ensuring a smooth and timely distribution.
- Life insurance policies can be assigned to specific beneficiaries, ensuring that the proceeds are paid directly to them, bypassing the estate.
Final Conclusion
In essence, the death benefit of life insurance is a testament to the love, care, and financial responsibility we hold for our loved ones. By carefully considering the factors that influence the death benefit and understanding its implications, we can harness its power to create a lasting legacy that protects and supports those who matter most.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the purpose of a death benefit?
The death benefit provides financial support to beneficiaries upon the policyholder’s death, covering expenses and ensuring financial stability.
How is the death benefit calculated?
The death benefit is typically determined by factors such as the policyholder’s age, health, occupation, and the type of life insurance policy.
What are the different types of death benefits?
Common types include lump sum, installment, and joint life policies, each with its unique characteristics and suitability for different circumstances.
How can I assign a death benefit?
Policyholders can designate beneficiaries and assign the death benefit to specific individuals or entities through the life insurance policy.
What are the tax implications of the death benefit?
Death benefits are generally tax-free for beneficiaries, but there may be tax implications for the estate if the death benefit exceeds certain thresholds.